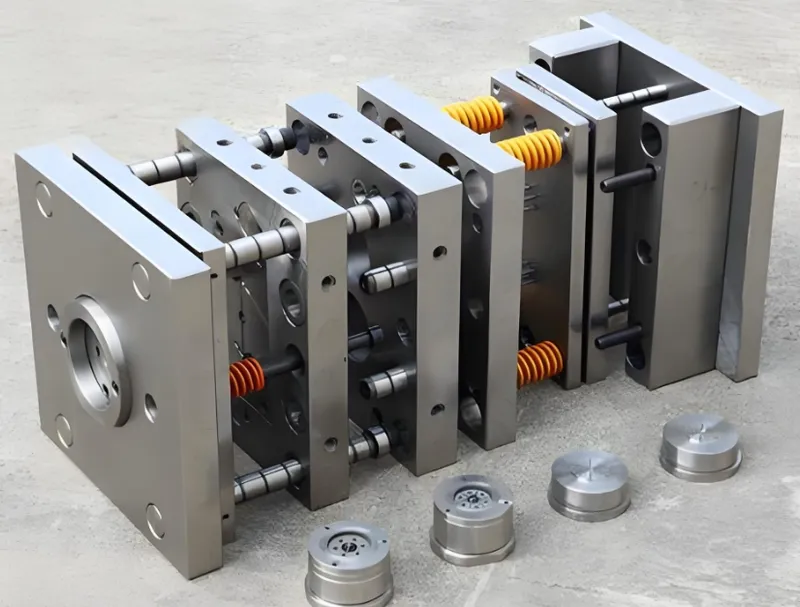
Rapid prototyping1 techniques for mold making have transformed manufacturing by enabling faster, more cost-effective mold production. These methods are vital for industries like automotive, medical devices, and consumer goods, where precision and speed are paramount.
Rapid prototyping for mold making2 involves quickly creating molds for manufacturing, primarily for injection molding, using techniques like 3D printing3, CNC machining, and prototype injection molding.
This article explores these techniques, offering a comprehensive guide to help you select the best method for your project, optimize production, and ensure high-quality molds.
3D printing is the fastest rapid prototyping technique for mold making.True
3D printing allows for rapid iteration and complex geometries, making it ideal for quick mold production.
CNC machining is only suitable for simple mold designs.False
CNC machining can handle complex designs, but it may be slower and more expensive for intricate molds compared to 3D printing.
- 1. What Are the Most Effective Rapid Prototyping Techniques for Mold Making?
- 2. How Do These Techniques Compare in Terms of Speed and Cost?
- 3. What Are the Typical Applications for Each Technique?
- 4. What Are the Key Steps in the Workflow for Each Technique?
- 5. How Do Different Materials Affect the Final Mold?
- 6. What Are the Process Limitations to Consider?
- 7. How to Choose the Right Technique for Your Project?
- 8. What Are the Related Technologies to Consider?
- 9. Conclusion
What Are the Most Effective Rapid Prototyping Techniques for Mold Making?
Rapid prototyping techniques are crucial for industries needing quick turnaround times and high precision. These methods create molds for producing multiple parts, bridging design and production.
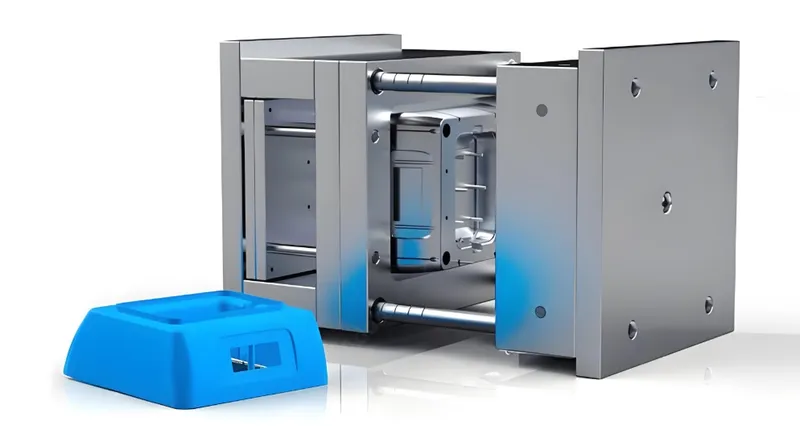

The most effective rapid prototyping techniques4 for mold making include 3D printing, CNC machining5, and prototype injection molding, each offering unique advantages in speed, cost, and material flexibility.
| Technique | Recommended Use Case | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 3D Printing | Complex designs, quick iterations | Ideal for small batches |
| CNC Machining | Material flexibility, precision | Suitable for specific materials |
| Prototype Injection Molding | Production-ready prototypes | Best for larger runs |
3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing)
3D printing builds molds layer by layer from digital models using techniques like Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)6, Stereolithography (SLA), and Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). It excels in creating complex, intricate molds requiring multiple iterations.
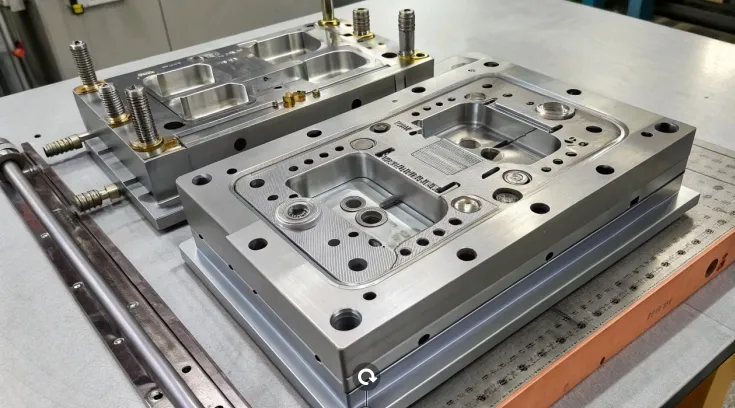

CNC Machining
CNC machining, a subtractive process, carves molds from solid blocks, offering high precision and material flexibility. It’s ideal for molds needing specific materials, such as metals.
Prototype Injection Molding
Prototype injection molding7 uses softer metals like aluminum or P20 steel to produce molds quickly and cheaply, with a shorter service life than traditional molds. It’s perfect for production-ready prototypes, especially simpler parts.
3D printing is the most cost-effective technique for mold making.False
While 3D printing has low upfront costs, it may not be cost-effective for large runs due to material limitations.
Prototype injection molding is suitable for all molds.False
It’s best for production-ready prototypes, not ideal for highly complex or small-batch molds.
How Do These Techniques Compare in Terms of Speed and Cost?
Choosing a technique depends on project needs like speed, cost, and materials.
3D printing offers the fastest turnaround and lowest upfront costs, CNC machining provides material flexibility, and prototype injection molding is cost-effective for larger runs.

Speed
-
3D Printing: Fastest for complex designs and iterations.
-
CNC Machining: Slower for intricate molds but precise.
-
Prototype Injection Molding: Requires tooling but efficient for larger runs.
Cost
-
3D Printing: Low initial costs, but material limits may raise expenses for big runs.
-
CNC Machining: No tooling costs, but slower throughput.
-
Prototype Injection Molding: Higher tooling costs, cost-effective for production prototypes.
CNC machining is the most expensive technique.False
While costly for complex molds, it’s economical for specific materials and precision.
Prototype injection molding reduces overall costs.True
It streamlines the transition to full production, lowering costs.
What Are the Typical Applications for Each Technique?
Each technique suits specific industries and products based on their characteristics.
3D printing fits medical devices and aerospace, CNC machining suits industrial equipment, and prototype injection molding serves automotive and consumer electronics.

3D Printing
-
Medical Devices: Custom molds for prosthetics and implants.
-
Aerospace: Lightweight, complex molds for aircraft parts.
CNC Machining
-
Industrial Equipment: Molds needing metals.
-
Tooling: Precision molds for tools.
Prototype Injection Molding
-
Automotive: Production molds for car parts.
-
Consumer Electronics: Molds for housings.
3D printing is only used in prototyping.False
It’s also used for direct part production in some cases.
CNC machining is the most versatile technique.True
It processes a wide range of materials, fitting various applications.
What Are the Key Steps in the Workflow for Each Technique?
Knowing each technique’s workflow ensures successful mold production.
3D printing involves design, slicing, printing, and post-processing; CNC machining includes design, CAM programming, machining, and finishing; prototype injection molding covers design, mold making, assembly, injection, and testing.
3D Printing Workflow
-
Design: Create a 3D mold model.
-
Slicing: Slice the model into layers.
-
Printing: Build the mold layer by layer.
-
Post-Processing: Remove excess material and finish.
CNC Machining Workflow
-
Design: Model the mold in 3D.
-
CAM Programming: Generate machining toolpaths.
-
Machining: Cut the mold from a block.
-
Finishing: Polish or treat the surface.
Prototype Injection Molding Workflow
-
Design: Model the part and mold.
-
Mold Design: Include parting lines, ejection, and cooling.
-
Mold Making: Machine cavities and cores.
-
Mold Assembly: Assemble components.
-
Injection Molding: Inject plastic into the mold.
-
Testing: Test parts and iterate.
3D printing requires less post-processing than CNC machining.False
It often needs significant post-processing like removing supports.
Prototype injection molding is the most complex workflow.True
It involves multiple steps, making it more complex.
How Do Different Materials Affect the Final Mold?
Material choice impacts mold durability, finish, and compatibility.
Plastics are common in 3D printing and injection molding, while metals suit CNC machining and investment casting, each offering unique properties.

Plastics
-
3D Printing: Nylon, photopolymers, ABS, PLA.
-
Injection Molding: ABS, polycarbonate, polypropylene.
Metals
-
CNC Machining: Aluminum, steel.
-
Investment Casting: Steel, aluminum.
Plastics are the only materials used in rapid prototyping.False
Metals are also used, especially in CNC and casting.
Material selection impacts durability and finish.True
Materials affect mold performance and quality.
What Are the Process Limitations to Consider?
Each technique has limitations to address during design.
3D printing limits material strength and finish, CNC machining struggles with complex designs, and prototype injection molding requires tooling and lacks flexibility.

3D Printing Limitations
-
Material strength: May not endure high pressures.
-
Surface finish: Needs post-processing.
CNC Machining Limitations
-
Design complexity: Intricate designs are costly.
-
Material waste: Subtractive process wastes material.
Prototype Injection Molding Limitations
-
Upfront tooling: Requires investment.
-
Design flexibility: Changes are costly.
3D printing is the most flexible for design changes.True
It allows quick iterations without high costs.
CNC machining produces the least waste.False
It generates waste, unlike additive methods.
How to Choose the Right Technique for Your Project?
Selection hinges on project needs, budget, and timeline.
Use 3D printing for complex designs and iterations, CNC machining for precision and materials, and prototype injection molding for production-ready runs.
Decision-Making Framework
-
High-volume production planned?
- Yes: Prototype injection molding.
- No: Next question.
-
Multiple iterations needed?
- Yes: 3D printing.
- No: Next question.
-
Specific material properties required?
- Yes: CNC machining.
- No: Weigh cost and speed.
Choice depends solely on cost.False
Material, complexity, and volume also matter.
Prototype injection molding is best for all projects.False
It’s ideal for production runs, not small or complex designs.
These techniques connect to a broader manufacturing ecosystem.
Related technologies include CAD software for design, CAM for CNC machining, and full production injection molding for high-volume output.
Upstream Technologies
-
CAD Software: Designs molds and parts.
-
CAM Software: Creates CNC toolpaths.
Downstream Technologies
-
Full Production Injection Molding: Scales from prototypes.
-
CNC Machining for Final Parts: Produces end-use parts.
CAD software is only used in 3D printing.False
It’s used across all techniques.
Full production injection molding is a rapid prototyping technique.False
It’s for high-volume production, not prototyping.
Conclusion
Rapid prototyping techniques like 3D printing, CNC machining, and prototype injection molding offer distinct benefits. Understanding their strengths and applications ensures efficient, cost-effective, and high-quality mold production tailored to your needs.
3D printing is the future of mold making.True
Advancements in materials and tech make it increasingly viable.
CNC machining will become obsolete due to 3D printing.False
It remains vital for precision and specific materials.
-
Explore how Rapid prototyping can enhance efficiency and reduce costs in manufacturing processes. ↩
-
Discover the cutting-edge techniques in mold making that can improve production quality and speed. ↩
-
Learn about the transformative impact of 3D printing on mold making and its advantages over traditional methods. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand various rapid prototyping techniques and their applications in mold making, enhancing your production efficiency. ↩
-
Learn about CNC machining’s precision and material flexibility, making it a vital technique in rapid prototyping. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand how SLS technology revolutionizes 3D printing with its unique layer-by-layer approach. ↩
-
Learn about prototype injection molding and its efficiency in creating quick, cost-effective molds for prototypes. ↩






