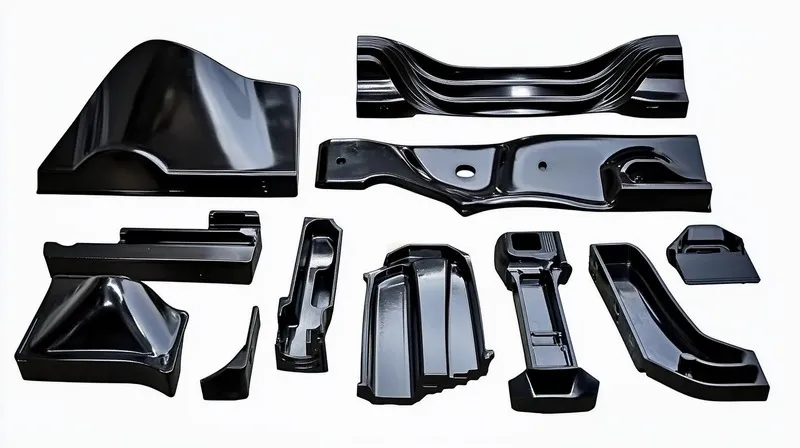
Injection molding has long been a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling the mass production of complex plastic parts with precision and efficiency. However, as global market trends evolve, the injection molding industry faces new challenges and opportunities. From the rise of electric vehicles1 to the push for sustainability2, these trends are reshaping how manufacturers approach production, material selection, and technology adoption. In this article, we’ll explore the impact of these global trends on the injection molding industry and what it means for the future.
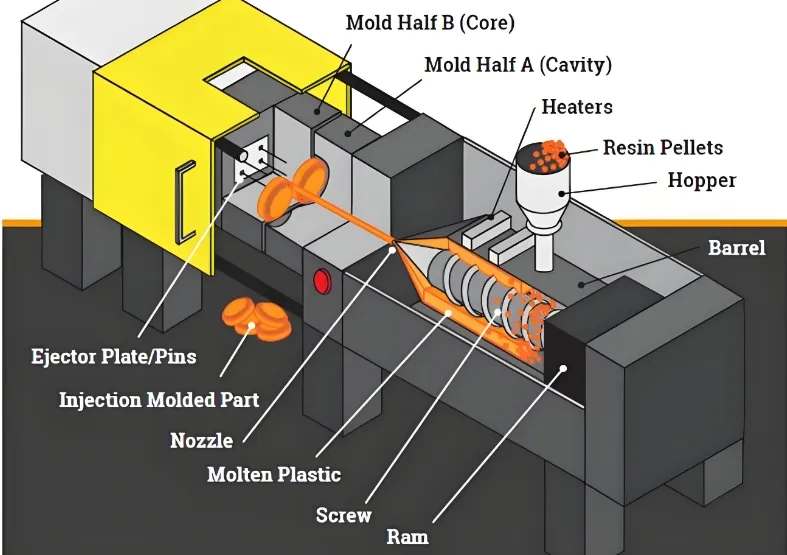
Injection molding is a manufacturing process where molten material is injected into a mold cavity, cooled, and solidified to form parts with specific shapes, widely used for high-volume production due to its efficiency and precision.
Understanding the intricacies of injection molding3 and its response to global trends is key to leveraging its benefits for your industry. Delve deeper to explore how economic, technological, and environmental factors are influencing the future of this essential manufacturing process.
Injection molding is the most versatile manufacturing process for plastic parts.True
It allows for the production of complex shapes with high precision and repeatability, making it suitable for a wide range of industries.
Injection molding is only used in the automotive industry.False
While automotive is a major sector, injection molding is also critical in packaging, consumer goods, medical devices, and electronics.
- 1. What is Injection Molding?
- 2. What are the Common Materials Used in Injection Molding?
- 3. What are the Steps in the Injection Molding Process?
- 4. What are the Key Global Trends Impacting the Injection Molding Industry?
- 5. What are the Applications of Injection Molding?
- 6. How Does Injection Molding Compare to Other Manufacturing Processes?
- 7. Conclusion
What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding, also known as plastic injection molding4, is a manufacturing process where molten material—typically plastic—is injected into a mold cavity, cooled, and solidified to form parts with specific shapes. It is widely used for high-volume production due to its efficiency, precision, and ability to produce complex geometries.
Table: Classification of Injection Molding
| Classification | Details |
|---|---|
| By Process | – Standard injection molding – Gas-assisted injection molding – Structural foam injection molding – Liquid silicone rubber (LSR) injection molding |
| By Materials | – Thermoplastics (e.g., polypropylene, ABS, PVC) – Thermosets (e.g., epoxy, polyurethane) – Elastomers (e.g., TPE, silicone) – Metals (for metal injection molding, MIM) |
| By Applications | – Automotive (e.g., dashboards, bumpers) – Packaging (e.g., containers, caps) – Consumer goods (e.g., toys, appliances) – Medical devices (e.g., syringes, IV components) – Electronics (e.g., housings, connectors) |
Injection molding is essential for producing complex plastic parts with high precision.True
The process allows for tight tolerances and repeatability, making it ideal for industries requiring exact specifications.
What are the Common Materials Used in Injection Molding?
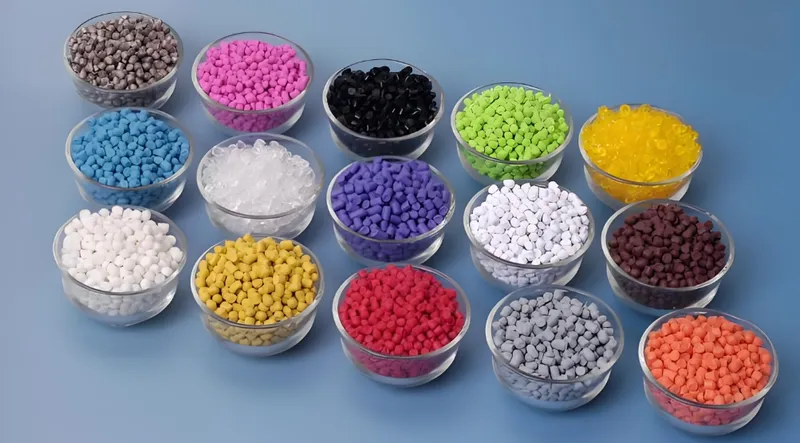
The choice of material in injection molding is critical, as it affects the part’s performance, cost, and environmental impact. Common materials include:

-
Thermoplastics: Such as polypropylene (PP), acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). These can be melted and reshaped multiple times, making them versatile and recyclable.
-
Thermosets: Like epoxy and polyurethane, which undergo a chemical change during molding, offering superior heat resistance but are less recyclable.
-
Elastomers: Including thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) and silicone, used for flexible parts like seals and grips.

Global trends, particularly the push for sustainability, are driving the adoption of eco-friendly materials such as bioplastics5 and recycled polymers6. For example, the use of polylactic acid (PLA) in packaging is growing due to its biodegradability, while recycled PET is increasingly used in consumer goods.
Sustainability trends are pushing injection molders to adopt biodegradable materials.True
Consumer demand and regulatory pressures are leading manufacturers to explore materials like PLA and bio-PET.
All materials used in injection molding are recyclable.False
While thermoplastics are recyclable, thermosets are not, due to their chemical structure.
What are the Steps in the Injection Molding Process?
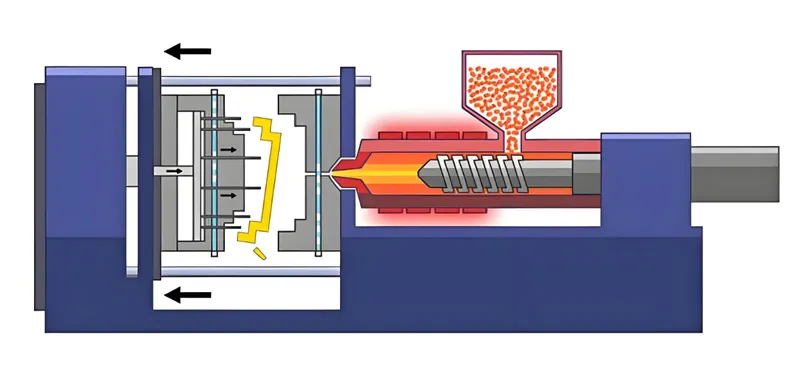
The injection molding process7 is pivotal in producing high-quality plastic parts efficiently. It consists of four main steps:
-
Clamping: The mold is closed and secured in the injection molding machine to withstand injection pressure8.
-
Injection: Molten material is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure, ensuring complete filling.
-
Cooling: The material is allowed to cool and solidify within the mold, with cooling time9 affecting cycle efficiency.
-
Ejection: The mold opens, and the solidified part is ejected, ready for further processing or use.
Key parameters include:
-
Injection pressure: Ensures proper filling of the mold.
-
Cooling time: Impacts cycle time and part quality.
-
Mold temperature: Influences material flow and part shrinkage.
Optimizing cooling time can significantly reduce production costs.True
Shorter cooling times lead to faster cycle times, increasing production efficiency.
What are the Key Global Trends Impacting the Injection Molding Industry?
Several global market trends are shaping the future of injection molding, influencing everything from material selection to production strategies:

Economic Trends
-
Automotive Sector Growth: The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) is driving demand for lightweight plastic components. For example, Hyundai’s new EV factory in Georgia, set to produce 300,000 EVs annually by 2025, will increase the need for injection-molded parts like dashboards and bumpers (Electric Vehicles Market).
-
Packaging Industry Expansion: The e-commerce boom, particularly in emerging economies, is boosting demand for injection-molded packaging products like thin-wall containers and caps (E-commerce Market).

Technological Trends
- Automation and Industry 4.010: The integration of AI, robotics, and IoT is enhancing efficiency and enabling the production of complex parts. For instance, Hehnke GmbH adopted the Arburg-GESTICA control system in 2022 to improve productivity (Injection Molding Market Report).
Environmental Trends
- Sustainability Focus11: Manufacturers are adopting biodegradable and recycled materials to meet consumer and regulatory demands. The EU’s sustainability reporting requirements are pushing companies to use materials like PLA and bio-PET (Sustainable Injection Molding Design).

Geopolitical Trends
- Reshoring and Nearshoring: Supply chain disruptions have encouraged reshoring to the U.S. and nearshoring to Mexico, with the U.S. holding over 80% of North America’s injection molding revenue in 2023 (Injection Molding Trends in 2023).
The rise of electric vehicles is a major driver for the injection molding industry.True
EVs require lightweight plastic components to improve efficiency, increasing demand for injection-molded parts.
Global trends have no impact on the injection molding industry.False
Economic, technological, environmental, and geopolitical trends are reshaping the industry in significant ways.
What are the Applications of Injection Molding?
Injection molding is used across various industries, each influenced by global trends:

-
Automotive: For interior components, bumpers, and under-the-hood parts. The shift to EVs is increasing demand for lightweight parts.
-
Packaging: For containers, caps, and thin-wall products. The e-commerce boom is driving growth in this sector.

-
Consumer Goods: For toys, appliances, and electronic housings. Sustainability trends are pushing for eco-friendly materials.
-
Medical Devices: For precision parts like syringes and IV components. The healthcare sector’s growth is boosting demand.
- Electronics: For connectors, housings, and other components. Technological advancements are enabling more complex designs.
Injection molding is essential for producing medical devices with high precision.True
The process allows for tight tolerances and repeatability, crucial for medical applications.
How Does Injection Molding Compare to Other Manufacturing Processes?
While injection molding is ideal for high-volume production of complex parts, other processes like 3D printing and CNC machining have their place:

-
3D Printing: Better for low-volume production and prototyping but slower and more expensive for mass production.
-
CNC Machining: Suitable for metal parts or when high precision is needed, but less efficient for complex plastic parts.
Global trends like the push for rapid prototyping and customization are making 3D printing more attractive for certain applications, but injection molding remains the go-to for large-scale production.
3D printing is replacing injection molding for mass production.False
While 3D printing is growing, it is not yet cost-effective for high-volume production compared to injection molding.
Conclusion
The injection molding industry is at a crossroads, with global market trends presenting both challenges and opportunities. From the rise of electric vehicles to the push for sustainability, manufacturers must adapt to stay competitive. By embracing new materials, technologies, and production strategies, the industry can continue to thrive in an ever-changing global landscape.
-
Learn about the significance of injection molding in the electric vehicle industry, a key area of growth and innovation. ↩
-
Discover insights on sustainability in manufacturing, which is crucial for adapting to market changes and meeting consumer expectations. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand how injection molding is evolving with new technologies and market demands, ensuring you stay ahead in manufacturing. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand the fundamentals of plastic injection molding and its significance in modern manufacturing processes. ↩
-
Learn about the role of bioplastics in promoting sustainability and their growing use in manufacturing. ↩
-
Discover how recycled polymers contribute to environmental sustainability and cost-effectiveness in production. ↩
-
Understanding the injection molding process is crucial for anyone involved in manufacturing, as it highlights efficiency and quality in production. ↩
-
Learning about injection pressure is vital for optimizing the molding process, ensuring quality and efficiency in production. ↩
-
Exploring the impact of cooling time can help improve production efficiency and part quality, essential for manufacturers. ↩
-
Learn about the transformative effects of automation and Industry 4.0 on production efficiency and innovation. ↩
-
This resource provides insights into how sustainability is shaping manufacturing practices and material choices. ↩






