Designing injection molded parts1 for seamless assembly is essential for efficient manufacturing and high-quality products. It ensures that parts fit together perfectly, reducing assembly time and costs while improving overall product reliability. This guide will walk you through the key principles, materials, and techniques to achieve seamless assembly2 in your injection molded parts.
Proper design of injection molded parts can reduce assembly time3 by up to 50%, leading to significant cost savings and faster production cycles.
Understanding the intricacies of injection molding and assembly design is crucial for optimizing your manufacturing process. Delve deeper to explore how different design choices and materials impact the final product’s assembly and performance.
Proper design of injection molded parts can reduce assembly time by up to 50%.True
By ensuring parts fit together seamlessly, manufacturers can minimize manual adjustments and errors during assembly, leading to faster production cycles.
Injection molding is only suitable for simple part designs.False
Injection molding can produce highly complex parts with intricate geometries, making it versatile for various applications.
- 1. What are the Key Design Principles for Seamless Assembly?
- 2. How Do You Choose the Right Materials for Injection Molded Parts?
- 3. What are the Steps in the Injection Molding Process for Seamless Assembly?
- 4. What are the Common Assembly Techniques for Injection Molded Parts?
- 5. How Can You Ensure Quality in Injection Molded Parts for Assembly?
- 6. Conclusion
What are the Key Design Principles for Seamless Assembly?
Designing for seamless assembly involves several critical principles that ensure parts fit together accurately and efficiently. These principles are rooted in Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA)4 practices.

Key design principles for seamless assembly include precise geometries5, alignment features6, uniform wall thickness, and draft angles, which collectively ensure parts fit together without gaps or misalignment.
| Design Principle | Recommended Practice | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Uniform Wall Thickness | Maintain 1.0–2.5 mm for ABS/PP | Prevents warping and sink marks |
| Draft Angles | Incorporate 1–2 degrees for easy ejection | Essential for mold release |
| Alignment Features | Use pins, guides, or clips | Ensures accurate part alignment |
| Tolerances | Specify ±0.05 mm for critical features | Ensures precise fit |
Precise Geometries
Designing parts with precise dimensions and consistent geometries is fundamental. This minimizes gaps and ensures a snug fit during assembly. Use CAD software to model parts accurately and simulate assembly processes.
Alignment Features
Incorporate features like pins, guides, or clips to aid in aligning parts during assembly. These features reduce the risk of misalignment and make the assembly process more intuitive.
Uniform Wall Thickness
Maintaining uniform wall thickness prevents warping and ensures even cooling, which is crucial for part stability and fit. For materials like ABS or polypropylene, aim for a thickness of 1.0–2.5 mm.

Draft Angles
Adding draft angles (typically 1–2 degrees) to vertical surfaces facilitates easy ejection from the mold, reducing the risk of part damage and ensuring consistent quality.
Uniform wall thickness is critical for preventing part warping.True
Even wall thickness ensures uniform cooling, reducing the likelihood of warping or sink marks.
Draft angles are unnecessary for injection molded parts.False
Draft angles are essential for easy mold release and to prevent part damage during ejection.
How Do You Choose the Right Materials for Injection Molded Parts?
Material selection plays a pivotal role in ensuring that injection molded parts are compatible, durable, and suitable for seamless assembly.
Common materials for injection molded parts include ABS, polypropylene, nylon, and polycarbonate, each offering unique properties like strength, flexibility, and thermal resistance.

Material Properties and Compatibility
-
Shrinkage: Materials like ABS have lower shrinkage rates, which is crucial for maintaining precise dimensions and ensuring parts fit together without gaps.
-
Thermal Expansion: Choose materials with similar coefficients of thermal expansion to prevent misalignment due to temperature changes.

- Durability: For high-stress applications, materials like nylon or polycarbonate provide excellent strength and wear resistance.
Material Selection Guide
| Material | Key Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| ABS | Low shrinkage, good impact resistance | Consumer electronics, automotive |
| Polypropylene | Flexible, chemical resistant | Packaging, medical devices |
| Nylon | High strength, wear resistant | Automotive, industrial parts |
| Polycarbonate | High impact strength, transparent | Optical lenses, safety equipment |
Selecting the right material involves balancing cost, performance, and assembly requirements. For example, softer plastics like polypropylene are ideal for snap-fit assemblies, while harder plastics like polycarbonate may require screws or other fasteners.
Material selection impacts both the manufacturing process and the final product's performance.True
Different materials have varying shrinkage rates, strength, and flexibility, which affect how parts fit together and perform in use.
All plastics are suitable for injection molding.False
Only thermoplastics and some thermosets can be injection molded; material choice depends on the application's specific requirements.
What are the Steps in the Injection Molding Process for Seamless Assembly?
The injection molding process must be carefully controlled to produce parts that assemble seamlessly. Each step impacts the final part’s quality and fit.
The injection molding process involves design, mold making, injection, cooling, ejection, and finishing, with each step critical for ensuring parts fit together perfectly.

Design and Simulation
-
CAD Modeling: Create detailed models incorporating DFMA principles.
-
Simulation: Use tools like Autodesk Moldflow to predict and resolve potential issues before production.
Mold Design and Fabrication
- Mold Components: Design the mold with core, cavity, runners, and gates to ensure even material flow.
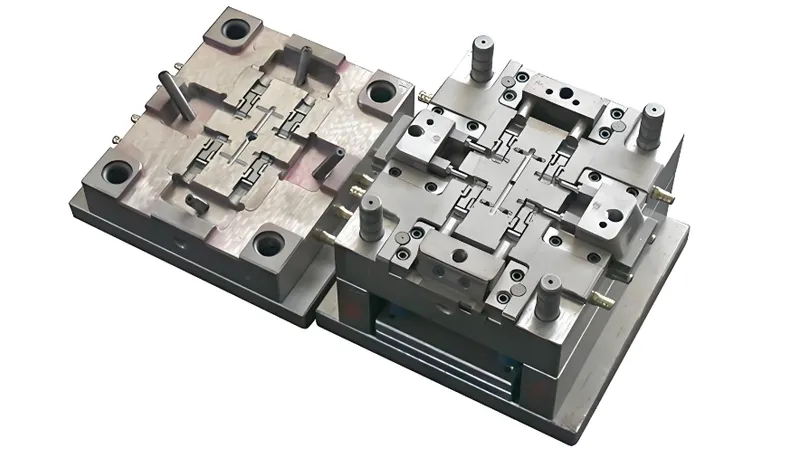
- Precision Machining: Use CNC or EDM to achieve tight tolerances.
Injection and Cooling
-
Injection Parameters: Control pressure and temperature to fill the mold completely.
-
Cooling Time: Ensure uniform cooling to prevent warping.
Ejection and Finishing
-
Ejection System: Design to avoid part damage during removal.
-
Secondary Operations: Perform trimming or assembly of inserts if needed.
Simulation tools can reduce the risk of design errors in injection molding.True
Simulation software helps identify potential issues like warping or incomplete filling before production, saving time and costs.
All injection molded parts require secondary operations.False
Many parts can be designed to be assembly-ready without additional finishing, depending on the application.
What are the Common Assembly Techniques for Injection Molded Parts?
Various assembly techniques7 can be used to join injection molded parts, each with its advantages and considerations.
Common assembly techniques include snap-fits8, screws, adhesives9, and welding, chosen based on the application’s requirements for strength, disassembly, and cost.

Snap-Fits
-
Advantages: No additional fasteners needed, quick assembly.
-
Considerations: Requires precise design to avoid breakage.
Screws and Fasteners
-
Advantages: Strong, allows for disassembly.
-
Considerations: Increases part count and assembly time.
Adhesives
- Advantages: Provides a strong bond, suitable for complex shapes.

- Considerations: May require curing time, not easily disassembled.
Welding
-
Advantages: Creates a permanent, strong bond.
-
Considerations: Requires specialized equipment, not suitable for all materials.
Snap-fits are the most cost-effective assembly technique.True
Snap-fits eliminate the need for additional fasteners, reducing material and labor costs.
Welding is suitable for all types of plastics.False
Welding is typically used for thermoplastics and requires compatible materials and proper equipment.
How Can You Ensure Quality in Injection Molded Parts for Assembly?
Quality assurance10 is vital to ensure that injection molded parts meet the required specifications for seamless assembly.
Quality in injection molded parts is ensured through precise design, material selection, process control, and rigorous testing, minimizing defects and ensuring a perfect fit.

Design Validation
-
Prototyping11: Use 3D printing or CNC machining to create prototypes for fit testing.
-
Simulation: Employ software to simulate the molding process and identify potential defects.
Process Control
- Parameter Monitoring: Track injection pressure, temperature, and cooling time to maintain consistency.

- Mold Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain molds to prevent wear-related defects.
Testing and Inspection
-
Dimensional Checks12: Use calipers or CMMs to verify part dimensions.
-
Functional Testing: Assemble parts to ensure they fit and function as intended.
Prototyping is essential for validating assembly designs.True
Prototypes allow for physical testing of fit and function, reducing the risk of costly errors in production.
All injection molded parts require extensive testing.False
While testing is important, well-designed parts with proper process controls may require less extensive testing.
Conclusion
Designing injection molded parts for seamless assembly requires a holistic approach that integrates precise design principles, strategic material selection, and meticulous process control. By adhering to best practices such as maintaining uniform wall thickness, incorporating alignment features, and selecting compatible materials, manufacturers can achieve efficient assembly, reduce costs, and deliver high-quality products. Advanced tools like simulation software and prototyping further enhance the design process, ensuring that parts fit together perfectly. Whether for automotive, consumer electronics, or medical devices, mastering these techniques is key to success in modern manufacturing.
-
Explore this resource to learn effective strategies for designing injection molded parts that enhance assembly efficiency and product quality. ↩
-
Discover how seamless assembly techniques can streamline your manufacturing process and lead to better product reliability. ↩
-
Find out innovative methods to significantly reduce assembly time, leading to cost savings and faster production cycles. ↩
-
Explore DFMA practices to enhance your design process, ensuring efficient assembly and manufacturing. ↩
-
Understanding the role of precise geometries can significantly improve your assembly efficiency and product quality. ↩
-
Learn about alignment features that can streamline your assembly process and reduce errors. ↩
-
Understanding various assembly techniques can help you choose the best method for your project, ensuring efficiency and effectiveness. ↩
-
Exploring snap-fits can reveal their benefits and limitations, helping you decide if they’re suitable for your design needs. ↩
-
Learning about adhesives can provide insights into their application and effectiveness in creating strong bonds for complex shapes. ↩
-
Understanding quality assurance in injection molding can enhance your knowledge of manufacturing standards and practices. ↩
-
Exploring prototyping techniques can provide insights into effective design validation and reduce production errors. ↩
-
Learning about dimensional checks can help ensure precision in manufacturing, leading to better product quality. ↩





