Injection molding is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling the mass production of precise plastic parts across industries like automotive, medical, and consumer goods. However, for businesses, understanding the cost per part1 is crucial—it directly impacts profitability, pricing, and production decisions. Calculating this cost involves several key factors, including the mold, materials, production volume, and machine operation. In this guide, we’ll break down each component, provide a step-by-step calculation method, and clarify common misconceptions to help you make informed manufacturing choices.
Injection molding creates precise plastic parts by injecting molten plastic into a mold, ideal for high-volume production in industries like automotive and medical, but calculating the cost per part is essential for profitability.
Understanding how to calculate the cost per part can optimize your production process and reduce expenses. Explore further to see how factors like mold design and material choice2 impact your bottom line.
Injection molding is only cost-effective for large production runs.False
While ideal for high volumes, injection molding can be economical for smaller runs with simpler molds or when precision is critical.
The mold cost is always the largest factor in the cost per part.False
For large production volumes, the mold cost per part decreases significantly, making material and operation costs more prominent.
What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a manufacturing process where molten plastic is injected into a custom mold3 under high pressure. Once cooled, the plastic solidifies into the desired shape, and the part is ejected. This method is favored for its ability to produce complex, high-precision parts quickly and consistently. Common applications include:
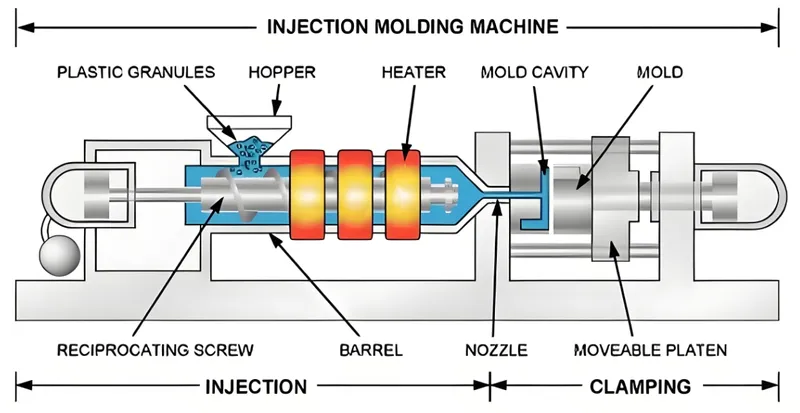
- Automotive: Dashboards, bumpers, and interior components.
- Medical: Syringes, surgical tools, and implants.
- Consumer Goods: Toys, kitchenware, and electronics housings.
- Packaging: Bottle caps, containers, and lids.
The process is highly scalable, making it ideal for both small batches and millions of units, depending on the mold and production setup.
What are the Key Factors in Calculating Cost Per Part?
Several factors influence the cost per part in injection molding. Understanding these can help you optimize your production strategy.

Mold Cost
The mold is the most significant upfront expense. It’s custom-made for each part and can range from $100 for simple 3D-printed molds to over $100,000 for complex, high-volume steel molds4. Factors affecting mold cost include:
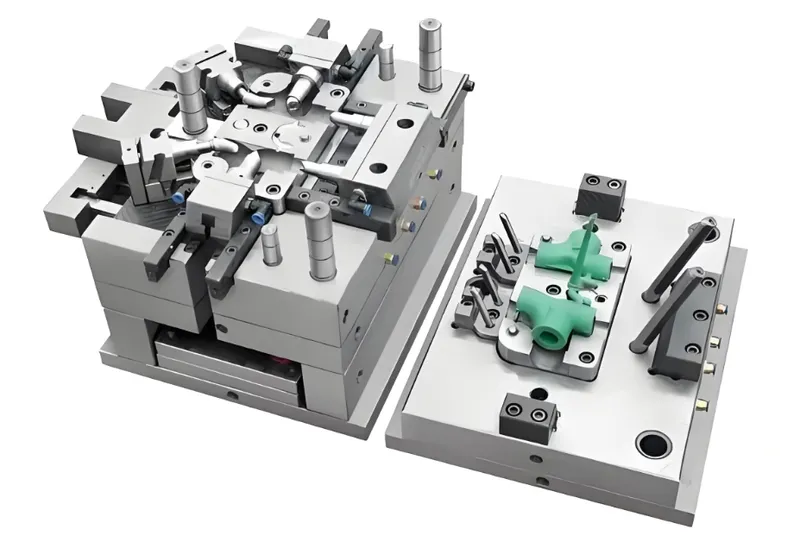
- Part Complexity: More intricate designs require sophisticated molds.
- Number of Cavities: Multi-cavity molds produce more parts per cycle but are costlier.
- Mold Material: Aluminum molds are cheaper but less durable than steel.
For small production runs, the mold cost can dominate, but for larger volumes, it’s spread across more parts, reducing the per-part cost.
Material Cost
The type of plastic used impacts both performance and cost. Common materials include:
| Plastic Type | Cost per kg | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | $2 – $5 | Durable, impact-resistant | Automotive, toys |
| Polypropylene (PP) | $1 – $3 | Flexible, chemical-resistant | Packaging, medical |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | $3 – $6 | Transparent, high heat resistance | Electronics, lenses |
| Polyethylene (PE) | $1 – $2 | Lightweight, moisture-resistant | Containers, bottles |
To calculate the material cost per part, multiply the part’s weight by the plastic’s cost per kilogram. For example, a 0.1 kg part made from ABS at $2.50/kg costs $0.25 in material.
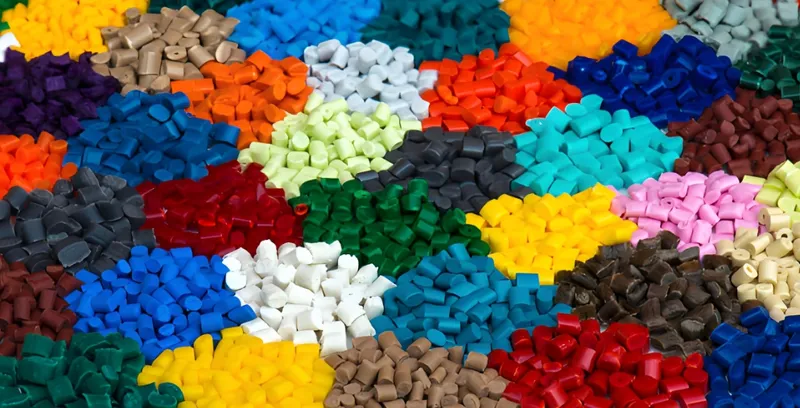

Production Volume
Production volume is critical because it determines how the mold cost is amortized. Higher volumes reduce the mold cost per part:
- For 1,000 parts with a $10,000 mold, the mold cost per part is $10.
- For 100,000 parts, it drops to $0.10 per part.
Thus, injection molding becomes more cost-effective as production scales.
Machine Operation Cost
This cost is based on the cycle time (time to produce one part) and the machine’s hourly rate5 (typically $20–$50). Shorter cycle times reduce costs. For example:
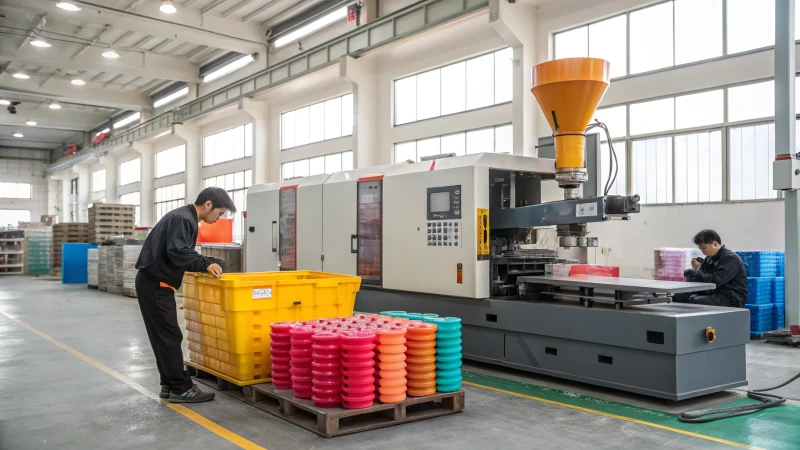

- Cycle time: 30 seconds (0.0083 hours)
- Machine rate: $30/hour
- Operation cost per part: 0.0083 × $30 = $0.25
Optimizing cycle time6 through efficient mold design can significantly lower costs.
Other Costs
Additional expenses may include:
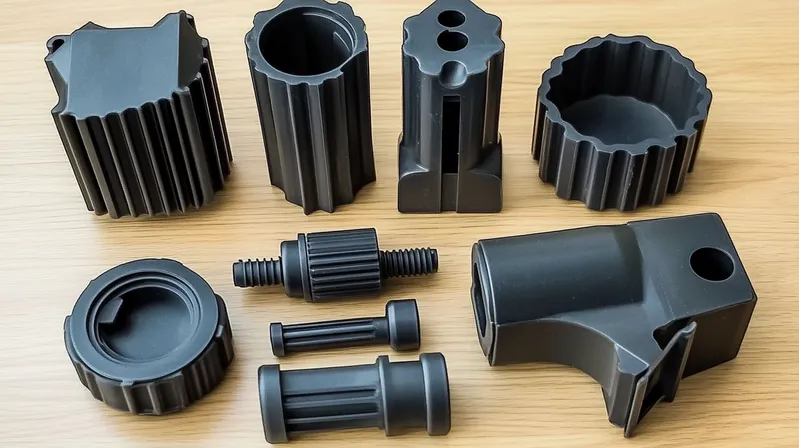

- Post-processing: Trimming, painting, or assembly.
- Quality Control: Inspections and testing.
- Packaging and Shipping: Preparing parts for delivery.
These vary by project but should be factored into the total cost.
Using cheaper materials always reduces the overall cost.False
Cheaper materials may require longer cycle times or more expensive molds, offsetting savings.
Injection molding is unsuitable for prototyping.False
While typically used for production, injection molding can be viable for prototypes with reusable or low-cost molds.
How Do You Calculate the Cost Per Part?
Calculating the cost per part involves summing the amortized mold cost, material cost7, machine operation cost, and other expenses. Here’s a step-by-step guide:

- Estimate Mold Cost: Get a quote or use historical data (e.g., $10,000).
- Calculate Material Cost Per Part: Part weight × plastic cost per kg (e.g., 0.1 kg × $2.50/kg = $0.25).
- Determine Machine Operation Cost: (Cycle time in hours) × machine hourly rate (e.g., 0.0083 hours × $30 = $0.25).
- Add Other Costs: Estimate additional expenses (e.g., $0.10 per part).
- Calculate Total Cost Per Part: (Mold cost / production volume) + material cost + operation cost + other costs.

Example Calculation:
- Mold Cost: $20,000
- Production Volume: 50,000 parts
- Material: ABS at $2.50/kg
- Part Weight: 0.05 kg
- Cycle Time: 20 seconds (0.0056 hours)
- Machine Rate: $40/hour
- Other Costs: $0.15/part
Calculations:
- Mold cost per part: $20,000 / 50,000 = $0.40
- Material cost: 0.05 kg × $2.50/kg = $0.125
- Operation cost: 0.0056 hours × $40 = $0.224
- Other costs: $0.15
Total Cost Per Part: $0.40 + $0.125 + $0.224 + $0.15 = $0.899 ≈ $0.90
This method provides a clear breakdown, helping you identify areas to optimize.
What are the Applications of Injection Molding?
Injection molding8’s versatility makes it indispensable across industries:

- Automotive: Produces lightweight, durable parts like dashboards and trim.
- Medical: Creates sterile, precise components like syringes and implants.
- Consumer Goods: Used for everyday items like toys and kitchenware.
- Packaging: Ideal for high-volume items like bottle caps and containers.
- Electronics: Manufactures housings and connectors with tight tolerances.
Its ability to handle complex designs and various materials makes it a go-to for many sectors.
How Does Injection Molding Compare to Other Processes?
While injection molding excels in high-volume production, it’s useful to compare it with alternatives:
| Process | Best For | Cost | Speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Injection Molding | High-volume plastic parts | Low per-part for large runs | Fast cycles, slow setup |
| 3D Printing | Prototypes, complex geometries | High per-part, low setup | Slow for volume |
| CNC Machining | Metal parts, low to medium volume | High per-part, no mold cost | Precise but slower |
Choose injection molding when you need scalability and precision9 for plastic parts.

Conclusion
Calculating the cost per part in injection molding is essential for managing production expenses and setting competitive prices. By understanding the impact of mold costs, material choices, production volume, and machine operation, you can make informed decisions that enhance profitability. Whether you’re producing a few thousand or millions of parts, mastering this calculation is key to optimizing your manufacturing process.
- Understanding the factors that influence cost per part can help you optimize your manufacturing process and improve profitability. ↩
- Learning about mold design and material choice can significantly impact your production costs and product quality. ↩
- Exploring the injection molding process will give you insights into its efficiency and applications in various industries. ↩
- Understanding the cost factors of injection molding molds can help you make informed decisions for your production needs. ↩
- Knowing the machine’s hourly rate helps in budgeting and optimizing production costs effectively. ↩
- Exploring the impact of cycle time on costs can lead to more efficient production strategies and savings. ↩
- Learning how to accurately calculate material costs can lead to better budgeting and cost management in production processes. ↩
- Exploring the advantages of injection molding can reveal its importance in various industries and its impact on production efficiency. ↩
- Discover why scalability and precision are crucial for successful manufacturing and how they impact production quality. ↩




