Injection molding is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling the mass production of precise plastic parts efficiently. However, one of the most pivotal decisions in this process is selecting the right material. This choice influences not just the performance of the final product but also the overall production costs1 significantly. In this blog post, we’ll explore how material selection impacts injection molding costs, covering foundational concepts, practical applications, technical details, and decision-making tools.
Material selection in injection molding directly affects production costs by influencing material prices, processing requirements, tooling longevity2, and part performance, critical for industries like automotive, medical, and consumer goods.
Understanding these dynamics can help manufacturers optimize costs while meeting quality and performance standards. Let’s dive into the details.
Material selection significantly impacts the cost of injection molding.True
Different materials have varying costs, processing requirements, and performance characteristics, all of which affect the overall cost of production.
- 1. What Is Injection Molding and Why Does Material Selection Matter?
- 2. How Does Material Selection Influence Costs in Real-World Applications?
- 3. What Are the Technical Factors Linking Materials to Costs?
- 4. What Practical Tools Can Guide Material Selection?
- 5. How Do Related Technologies Connect to Material Selection?
- 6. Conclusion
What Is Injection Molding and Why Does Material Selection Matter?
Injection molding involves injecting molten material into a mold cavity, where it cools and solidifies into a precise shape. The process is widely used for producing plastic parts across industries.
Injection molding3 uses molten polymers injected into molds to create precise parts, with material selection determining cost, quality, and efficiency.
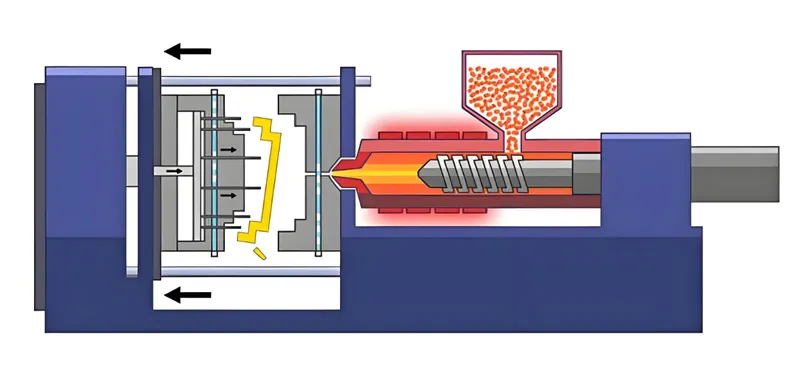
Key Material Types
-
Thermoplastics4: Re-meltable polymers like ABS, polycarbonate (PC), and polypropylene (PP), prized for versatility and recyclability.
-
Thermosets: Permanently set polymers like epoxy and phenolic resins, offering high heat resistance and stability.
-
Commodity Plastics: Affordable options like PP and polyethylene (PE) for general use.
-
Engineering Plastics5: High-performance, costly materials like PEEK and Ultem for specialized applications.
Material selection matters because it dictates:

-
Part Properties: Strength, flexibility, heat resistance.
-
Process Efficiency: Cycle time, energy use.
-
Cost: From raw material price to tooling wear.
All materials are equally suitable for injection molding.False
Materials must be compatible with the process, and not all plastics can be molded effectively or economically.
How Does Material Selection Influence Costs in Real-World Applications?
Material choice varies by industry, balancing cost with performance needs.
Material selection in injection molding varies by application, impacting costs in automotive (lightweight, durable materials6), medical (biocompatible options7), and consumer goods (cost-effective, aesthetic materials8).

Application Examples
-
Automotive: PP and ABS reduce weight and cost for parts like bumpers, while PC offers durability for lenses.
-
Medical: PEEK and Ultem ensure biocompatibility and sterilization resistance, albeit at a higher cost.

- Consumer Goods: ABS provides a balance of strength, finish, and affordability for items like housings.
Comparing Technologies
| Process | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Injection Molding | High-volume, low per-unit cost | High tooling cost, material limits |
| CNC Machining | Low setup cost, broad material use | Slow for high volumes |
| 3D Printing | Design flexibility, no tooling | Higher cost, less durable parts |
Choosing a cheaper material always reduces overall costs.False
While material cost may drop, processing challenges or higher defect rates can increase total expenses.
What Are the Technical Factors Linking Materials to Costs?
The injection molding process involves several stages, each influenced by the material chosen.
Injection molding melts plastic, injects it into a mold, cools it, and ejects the part, with material properties affecting energy use, cycle time, and tooling costs.

Process Breakdown
-
Melting: Material is heated (e.g., 200–300°C for thermoplastics).
-
Injection: Molten plastic fills the mold (10,000–20,000 psi).
-
Cooling: Part solidifies (10–60 seconds, material-dependent).
- Ejection: Finished part is removed.
Material Impact on Costs
| Material | Cost Range | Processing Notes | Tooling Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | Low | Easy to process, low melting point9 | Minimal wear |
| PP | Low | Quick cooling, high shrink | May need adjustments |
| PC | Medium | Requires drying, higher pressure10 | Moderate wear |
| PEEK | High | High temperature, difficult to mold11 | Increased wear if abrasive |
-
Energy Use: High-melting-point materials (e.g., PEEK) consume more power.
-
Cycle Time: Slow-cooling materials (e.g., thick PC parts) extend production time.
-
Tooling Wear: Abrasive materials (e.g., glass-filled resins) require costly steel molds.
Engineering plastics like PEEK are only used in high-end applications.True
Their high cost restricts them to applications needing superior properties.
What Practical Tools Can Guide Material Selection?
Choosing the right material involves balancing cost and performance with actionable tools.
Practical tools for material selection in injection molding include checklists and decision guides to optimize cost and performance.

Design Checklist
-
Function: Match material to strength, heat, or chemical needs.
-
Volume: High volumes favor low-cost materials; low volumes prioritize ease.
-
Budget: Balance material and processing costs.
-
Regulations: Ensure compliance (e.g., biocompatibility for medical).
Decision Guide
- Define part requirements (e.g., durability, aesthetics).

-
Shortlist materials based on properties and cost.
-
Assess processing impacts (e.g., cycle time, mold wear).
-
Test via prototyping if feasible.
-
Select the optimal material.
Material selection ties into a broader manufacturing ecosystem.
Material selection in injection molding links to upstream material science and downstream finishing processes, enhancing cost-effectiveness and performance.

-
Upstream: Polymer chemistry develops cost-effective, high-performance materials.
-
Downstream: Finishing (e.g., painting) and assembly (e.g., welding) refine parts.
-
Complementary: CNC machining for prototypes, 3D printing for custom parts.
Conclusion
Material selection is a linchpin in injection molding, driving costs through raw material prices, processing demands, and tooling longevity. By leveraging application insights, technical knowledge, and practical tools, manufacturers can optimize their choices. Whether it’s ABS for affordable consumer goods or PEEK for critical medical devices, the right material aligns cost with quality.
-
Exploring how production costs vary with material choice can lead to better financial decisions in manufacturing. Check out this link for detailed analysis. ↩
-
Tooling longevity is crucial for cost efficiency in injection molding. Discover the factors that affect it to enhance your manufacturing process. ↩
-
Understanding injection molding is crucial for grasping its applications and benefits in manufacturing. ↩
-
Exploring thermoplastics will reveal their versatility and importance in various industries, enhancing your knowledge of material choices. ↩
-
Learning about engineering plastics can help you understand their specialized applications and why they are chosen for high-performance needs. ↩
-
Learn about innovative materials that enhance performance and reduce costs in the automotive industry by visiting this link. ↩
-
Explore this link to discover essential biocompatible materials that ensure safety and effectiveness in medical applications. ↩
-
This resource will guide you through materials that balance affordability and aesthetics, crucial for consumer product design. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand why ABS is favored for its ease of processing and low melting point, making it ideal for various applications. ↩
-
Learn about the significance of drying in PC processing and how it affects the quality and performance of the final product. ↩
-
Discover the complexities of working with PEEK, including its high-temperature requirements and molding difficulties, crucial for advanced applications. ↩






