Injection molding is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, producing everything from food packaging to life-saving medical devices. However, when these products come into contact with food or the human body, they must meet strict safety standards set by the U.S. Food and Drug
Administration (FDA). Achieving FDA compliance1 in injection molding is not just about using the right materials—it’s a comprehensive process that ensures every aspect of production meets regulatory requirements. This blog explores how injection molding companies navigate these complexities to deliver safe, compliant products.
Achieving FDA compliance in injection molding requires using FDA-approved materials2, adhering to stringent manufacturing practices3, and maintaining meticulous documentation to ensure product safety for food contact and medical applications.
Understanding the nuances of FDA compliance can help you make informed decisions when selecting a manufacturing partner or designing products for regulated industries. Explore the details below to see how different materials, processes, and regulations come together to meet these critical standards.
Using FDA-approved materials is the only requirement for achieving compliance in injection molding.False
While using approved materials is essential, companies must also adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), maintain clean production environments, and keep detailed records to ensure full compliance.
FDA compliance is mandatory for both food contact products and medical devices produced through injection molding.True
Both categories must meet FDA standards, though they are governed by different regulations—food contact under 21 CFR Parts 170-186 and medical devices under 21 CFR 820.
- 1. What are the Common Materials Used in FDA-Compliant Injection Molding?
- 2. What are the Steps in Achieving FDA Compliance for Injection Molding?
- 3. What are the Applications of FDA-Compliant Injection Molding?
- 4. What are the Differences Between FDA Compliance for Food Contact and Medical Devices?
- 5. Conclusion
What are the Common Materials Used in FDA-Compliant Injection Molding?
Selecting the right materials is the foundation of FDA compliance in injection molding, as these materials must meet stringent safety criteria for food contact and medical applications.

Common materials include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and polyetheretherketone (PEEK), chosen for their chemical resistance4, durability, and biocompatibility5.
| Material Type | Applications | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | Food packaging, containers | Flexible, moisture-resistant |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Medical syringes, food containers | Heat-resistant, sterilizable |
| Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) | Implants, surgical tools | Biocompatible, high strength |
Polyethylene (PE)
PE is a staple in food packaging due to its flexibility and resistance to moisture. It is listed in 21 CFR as an approved material for food contact, making it ideal for products like containers and lids.
Polypropylene (PP)
PP is versatile, used in both food and medical applications. Its ability to withstand high temperatures and sterilization processes makes it perfect for syringes and food containers that require durability and safety.

Polyetheretherketone (PEEK)
PEEK is a high-performance plastic favored in medical devices like implants and surgical tools. Its biocompatibility and strength ensure it meets the rigorous demands of medical applications.
Polyethylene is commonly used in FDA-compliant injection molding for food contact.True
PE is widely used due to its flexibility, moisture resistance, and FDA approval for food contact.
All plastics are suitable for FDA-compliant medical devices.False
Only specific plastics like PEEK and PP, which meet biocompatibility and sterilization standards, are suitable for medical applications.
What are the Steps in Achieving FDA Compliance for Injection Molding?
Achieving FDA compliance in injection molding is a multi-step process that ensures every aspect of production meets regulatory standards for safety and quality.
The process involves selecting FDA-approved materials, implementing Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), conducting rigorous testing, and maintaining detailed documentation for traceability.

Material Selection
Choose materials from FDA-approved lists, such as those in 21 CFR Parts 170-186 for food contact or biocompatible materials for medical devices.
Mold Design and Manufacturing
Design molds to prevent contamination and ensure smooth surfaces, especially for food contact products. For medical devices, molds must achieve tight tolerances for precision.
Injection Molding Process
Follow GMP to maintain clean production environments. For medical devices, production often occurs in clean rooms to prevent contamination.
Testing and Validation
Conduct tests like migration studies for food contact materials or biocompatibility tests for medical devices to ensure safety.

Documentation and Traceability
Keep detailed records of materials, processes, and test results to demonstrate compliance during FDA audits.
Documentation is a critical part of FDA compliance in injection molding.True
Thorough records ensure traceability and demonstrate adherence to FDA standards.
Clean room production is only necessary for medical devices, not for food contact products.False
While clean rooms are essential for medical devices, food contact products also require clean manufacturing environments to prevent contamination.
What are the Applications of FDA-Compliant Injection Molding?
FDA-compliant injection molding6 is essential across industries where product safety is paramount, particularly in food and healthcare sectors.
Applications include food packaging, medical devices, and pharmaceutical components, where compliance ensures safety and regulatory approval.

Food Packaging
Injection molding produces containers, lids, and utensils that must prevent chemical migration into food7. Materials like PE and PP are commonly used for their safety and durability.
Medical Devices
From syringes to implants, medical devices require biocompatible materials8 and sterile production environments. PEEK and PP are often chosen for their ability to meet these demands.
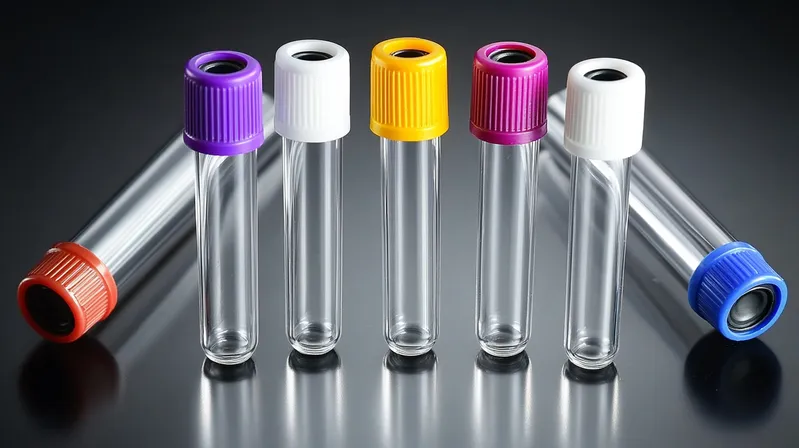

Pharmaceutical Components
Injection-molded parts like vials and closures must maintain product integrity and prevent contamination, adhering to strict FDA guidelines.
FDA-compliant injection molding is only used in the medical industry.False
While crucial for medical devices, it is also essential for food packaging and pharmaceutical components.
Injection molding is the preferred method for producing FDA-compliant products due to its precision and scalability.True
Injection molding offers high precision and cost-effectiveness for large-scale production, making it ideal for regulated industries.
What are the Differences Between FDA Compliance for Food Contact and Medical Devices?
While both food contact and medical device applications require FDA compliance, the specific regulations and requirements differ based on the product’s intended use.
Food contact compliance focuses on preventing chemical migration, while medical device compliance emphasizes biocompatibility, sterility, and device classification.

Regulatory Framework
- Food Contact: Governed by 21 CFR Parts 170-186, focusing on material safety and migration testing.
- Medical Devices: Regulated under 21 CFR 820, with additional standards like ISO 13485 for quality management.
Manufacturing Requirements
-
Food Contact: Requires clean manufacturing environments and GMP to prevent contamination.
-
Medical Devices: Often demands clean room production and stringent sterilization processes.

Testing and Validation
-
Food Contact: Migration tests ensure no harmful substances leach into food.
-
Medical Devices: Biocompatibility and sterility tests are critical, especially for higher-risk devices.
Medical devices require more stringent FDA compliance than food contact products.True
Medical devices, especially Class II and III, face stricter regulations due to their direct impact on patient health.
Both food contact and medical device compliance require material testing.True
Testing ensures materials are safe for their intended use, whether for food contact or medical applications.
Conclusion
Achieving FDA compliance in injection molding is a complex but essential process for ensuring the safety and quality of products used in food contact and medical applications1. By selecting the right materials, adhering to strict manufacturing practices2, and maintaining thorough documentation, companies can navigate the regulatory landscape and deliver compliant products. Whether you’re in the food packaging or medical device industry, understanding these requirements is key to success.
-
Understanding FDA compliance is crucial for ensuring product safety in manufacturing, especially for food and medical applications. ↩ ↩
-
Exploring FDA-approved materials helps ensure that your products meet safety standards for food and medical use. ↩ ↩
-
Learning about best manufacturing practices can guide you in maintaining compliance and ensuring product safety. ↩
-
Chemical resistance is vital for the longevity and safety of molded products. Discover more about its significance in this context. ↩
-
Biocompatibility is essential for materials used in medical applications. Learn more about its importance and implications. ↩
-
Understanding FDA-compliant injection molding is crucial for ensuring product safety in food and healthcare sectors. Explore this link for detailed insights. ↩
-
Chemical migration can pose serious health risks. Learn more about its implications and prevention methods to ensure food safety. ↩
-
Biocompatible materials are vital for patient safety in medical devices. Discover more about their applications and benefits in this informative resource. ↩






