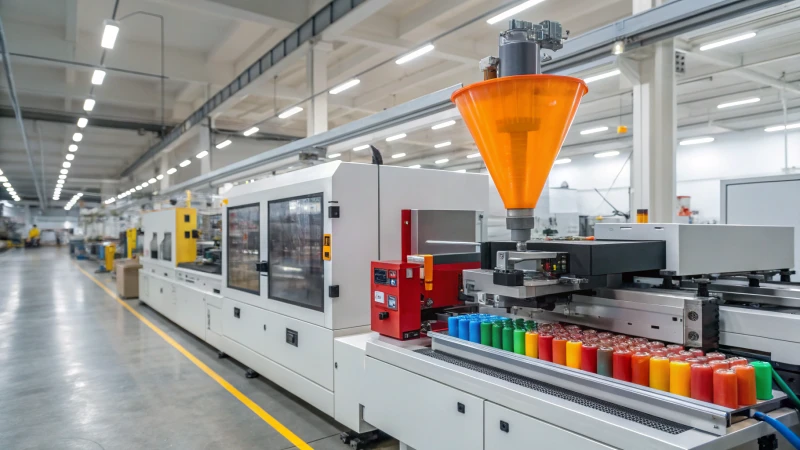
Injection molding is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling the mass production of precise plastic parts. A critical aspect of optimizing this process is the use of multi-cavity molds, such as 6 cavity molds1, which produce six identical parts in a single cycle. This capability can significantly enhance production rates, but it also introduces complexities that must be carefully managed to maintain efficiency and quality.
Injection molding with 6 cavity molds can greatly enhance production efficiency for medium to high-volume manufacturing by producing multiple parts per cycle, but it requires precise control over mold design and process parameters to ensure consistent quality across all cavities.
Understanding how to balance output and quality is key for manufacturers considering 6 cavity molds. This blog explores the efficiency of operating an injection molding machine with these molds, delving into materials, process steps, key factors, applications, and comparisons to other mold types.
Using a 6 cavity mold always results in six times the production rate of a single-cavity mold.False
While a 6 cavity mold produces six parts per cycle, cycle times may increase due to the need for balanced filling and cooling, and setup or maintenance time can further impact overall efficiency.
6 cavity molds are more cost-effective than single-cavity molds for all production volumes.False
For low volumes, the higher initial cost of a 6 cavity mold may not be offset by production gains, making single-cavity molds more economical.
Properly designed 6 cavity molds can achieve uniform part quality across all cavities.True
With balanced runner systems and uniform cooling, consistent quality across all six parts is achievable.
- 1. What Materials are Commonly Used in Injection Molding with 6 Cavity Molds?
- 2. What are the Steps in the Injection Molding Process with 6 Cavity Molds?
- 3. What are the Key Factors Affecting the Efficiency of Injection Molding with 6 Cavity Molds?
- 4. What are the Typical Applications of 6 Cavity Molds in Injection Molding?
- 5. How Do 6 Cavity Molds Compare to Single-Cavity and Other Multi-Cavity Molds?
- 6. Conclusion
What Materials are Commonly Used in Injection Molding with 6 Cavity Molds?
Material selection plays a pivotal role in the efficiency of injection molding with 6 cavity molds, influencing flow, cooling, and part quality.

Common materials include polypropylene (PP), acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), and polycarbonate (PC), chosen for their versatility, flow properties, and suitability for multi-cavity production.
| Material | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene (PP)2 | Good flow, low cost, chemical resistance | Automotive parts, containers |
| ABS | Strength, flexibility, impact resistance | Electronic housings, toys |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | High impact resistance, transparency | Medical devices, lenses |
Polypropylene (PP)
PP is favored for its excellent flow properties, allowing it to fill multiple cavities evenly. Its low cost and durability make it ideal for automotive components and consumer goods. However, its shrinkage requires precise mold design to maintain uniformity.

Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
ABS provides a balance of strength and flexibility, suitable for durable parts like electronic housings. Its moderate viscosity demands careful control of injection parameters to ensure consistent cavity filling.
Polycarbonate (PC)
PC is valued for its toughness and clarity, often used in medical and optical applications. Its higher viscosity requires optimized runner systems and injection pressures to achieve efficiency in a 6 cavity mold.
Material choice directly affects cycle time and part quality, necessitating adjustments in process settings for optimal efficiency.
Material choice has no impact on 6 cavity mold efficiency.False
Materials vary in viscosity, shrinkage, and cooling rates, all of which influence the efficiency and quality of multi-cavity molding.
Polypropylene’s flow properties enhance efficiency in 6 cavity molds.True
PP’s low viscosity aids uniform cavity filling, reducing defects and cycle time.
What are the Steps in the Injection Molding Process with 6 Cavity Molds?
Efficiency with 6 cavity molds depends on a well-executed injection molding process3, adapted to handle multiple cavities.
The process involves clamping, injection, cooling, and ejection, with efficiency reliant on uniform filling and cooling across all six cavities.
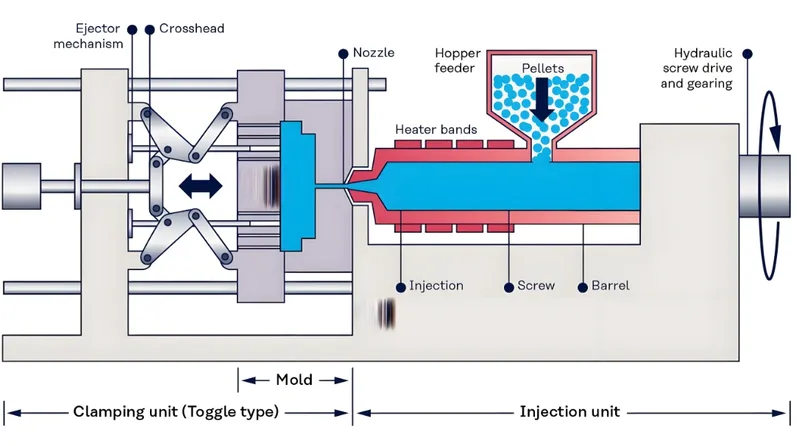
Clamping
The mold is clamped shut under high pressure to prevent leakage. Uniform clamping force ensures all cavities are sealed, avoiding defects like flash.
Injection
Molten plastic is injected through a runner system, distributing material to all six cavities. Balanced flow is critical to prevent variations in part quality.
Cooling
The plastic cools and solidifies, with uniform cooling4 across cavities essential to minimize cycle time and avoid warpage. Efficient cooling channel design is key.
Ejection
The mold opens, and the six parts are ejected simultaneously. A well-designed ejection system prevents damage to parts.
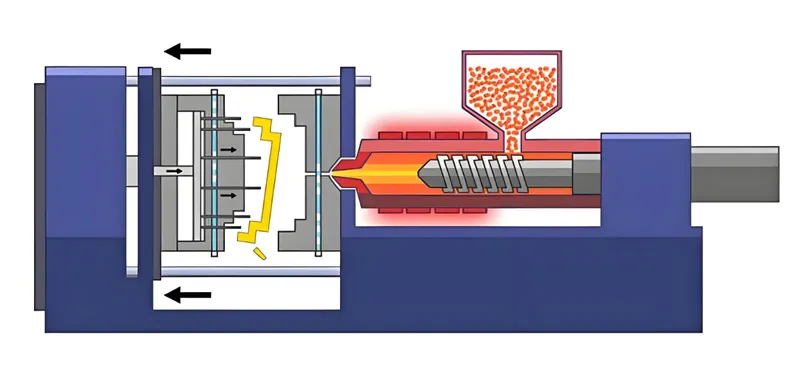
Cycle Repeat
The process repeats, producing six parts per cycle. Efficiency is optimized by minimizing cycle time while maintaining quality.
Precision in each step ensures that all cavities perform identically, maximizing output.
Cycle time is identical for single and 6 cavity molds.False
Multi-cavity molds often have longer cycle times due to the complexity of filling and cooling multiple cavities.
Balanced runner systems are essential for 6 cavity molds.True
They ensure equal material distribution, maintaining part consistency.
What are the Key Factors Affecting the Efficiency of Injection Molding with 6 Cavity Molds?
Several factors determine how efficiently a 6 cavity mold operates, requiring careful optimization.
Mold design5, machine parameters, material properties, and maintenance are critical to achieving high efficiency and quality.
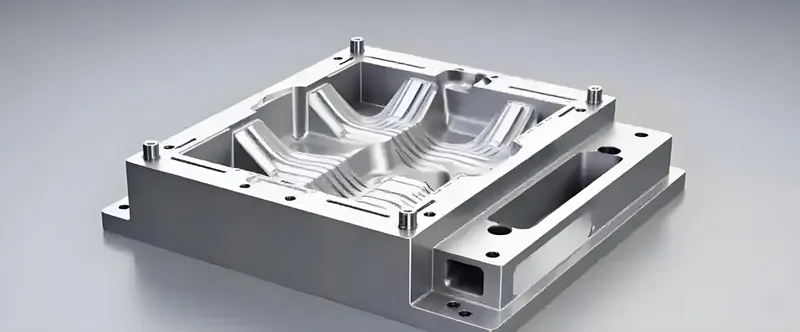
Mold Design
-
Balanced Runner System: Ensures equal flow to each cavity.
-
Cooling Channels: Promote uniform cooling, reducing cycle time.
-
Venting: Prevents air traps that could cause defects.
Machine Parameters
-
Injection Pressure/Speed6: Must fill all cavities without over-pressurizing.
-
Temperature Control: Maintains material consistency and cooling rates.
Material Properties
- Viscosity: Affects flow and filling efficiency.

- Shrinkage: Impacts dimensional accuracy across cavities.
Maintenance and Setup
-
Mold Maintenance: Prevents wear-related defects.
-
Setup Time: Quick changes minimize downtime.
Optimizing these elements enhances production rates and part quality.
Mold design is irrelevant to 6 cavity mold efficiency.False
Design elements like runners and cooling directly impact filling and cycle time.
Maintenance is key to sustained efficiency.True
Regular upkeep reduces downtime and ensures consistent performance.
What are the Typical Applications of 6 Cavity Molds in Injection Molding?
6 cavity molds excel in industries needing high volumes of small to medium-sized parts.
Applications include automotive components, medical devices, and consumer goods, leveraging the efficiency of multi-cavity production7.

Automotive Industry
Used for connectors, clips, and trim parts, benefiting from high output and consistency.
Medical Industry
Produces syringe barrels, caps, and disposables, requiring precision and volume.

Consumer Goods
Makes bottle caps, toys, and enclosures, reducing per-part costs8.
These sectors capitalize on the scalability of 6 cavity molds.
6 cavity molds are exclusive to automotive use.False
They are also used in medical and consumer goods industries.
6 cavity molds suit high-volume production of small parts.True
Their multi-part output is ideal for large-scale manufacturing.
How Do 6 Cavity Molds Compare to Single-Cavity and Other Multi-Cavity Molds?
Comparing mold types highlights the trade-offs in efficiency and cost.

6 cavity molds offer higher production rates than single-cavity molds but require more complex design and control, suiting medium to high-volume needs.
| Feature | Single-Cavity Mold | 6 Cavity Mold | Other Multi-Cavity Molds (e.g., 2 or 4) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Production Rate | Low (1 part/cycle) | High (6 parts/cycle) | Moderate (2-4 parts/cycle) |
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher | Moderate |
| Complexity | Simpler | More complex | Varies |
| Quality Control | Easier | More challenging | Depends on cavities |
| Best for | Low-medium volumes | Medium-high volumes | Flexible volumes |
Production Rate
6 cavity molds significantly outpace single-cavity molds but may have longer cycle times than smaller multi-cavity molds.

Cost
Higher upfront costs are offset by lower per-part costs in large runs.
Complexity
Increased design and control needs make 6 cavity molds best for high-volume scenarios.
6 cavity molds are always superior.False
They excel in high volumes but may be overkill for small runs.
Single-cavity molds simplify quality control.True
Fewer cavities reduce variability risks.
Conclusion
Injection molding with 6 cavity molds offers a robust solution for boosting production efficiency[^91], producing multiple parts per cycle. Success hinges on precise mold design, process control, and material selection to ensure quality across all cavities. For medium to high-volume production9, the benefits—higher output and lower per-part costs—often outweigh the challenges, making 6 cavity molds a valuable choice in automotive, medical, and consumer goods manufacturing.
-
Explore the advantages of 6 cavity molds to understand how they can boost your production efficiency and quality. ↩
-
Learn about Polypropylene’s unique properties and its applications in injection molding to enhance your material selection process. ↩
-
Understanding the injection molding process is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and part quality. Explore this resource for detailed insights. ↩
-
Learn why uniform cooling is essential for minimizing defects and ensuring high-quality parts in injection molding processes. ↩
-
Exploring best practices in mold design can significantly enhance your understanding of efficiency and quality in production. ↩
-
Understanding the impact of injection pressure and speed is crucial for optimizing production processes and achieving high-quality outputs. ↩
-
Discover the advantages of multi-cavity production, a key factor in achieving high output and cost-effectiveness in manufacturing. ↩
-
Understanding the factors affecting per-part costs can help you make informed decisions for cost-effective manufacturing. ↩
-
Discover best practices for medium to high-volume production to maximize output and maintain quality in manufacturing processes. ↩





