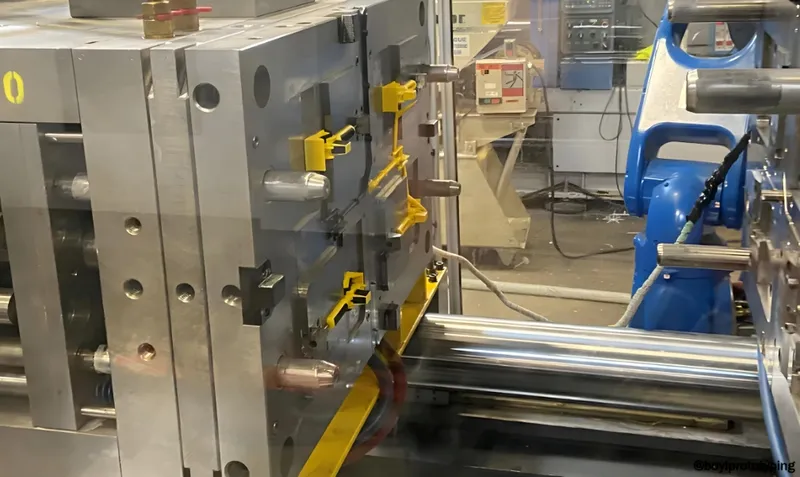
Thin-wall injection molding1 is a specialized manufacturing process that produces lightweight plastic parts with walls often less than 1mm thick, making it ideal for industries like packaging, automotive, and consumer electronics. However, designing molds for this process requires precision to ensure uniform filling, defect prevention, and efficient production.
Thin-wall injection molding creates lightweight parts with walls under 1mm, using high-speed injection to fill thin cavities, but requires precise mold design2 to avoid defects like warping or sink marks.
Understanding the intricacies of mold design for thin-wall injection molding is essential for manufacturers aiming to reduce material costs and improve production efficiency. Explore further to learn how material selection3, gate placement, and cooling systems impact the success of this process.
Thin-wall injection molding reduces material usage in manufacturing.True
By producing parts with thinner walls, less plastic is required, leading to significant cost savings.
Thin-wall injection molding is only suitable for simple part geometries.False
While challenging, thin-wall molding can be applied to complex parts with careful mold design and process control.
- 1. What is Thin-Wall Injection Molding?
- 2. What are the Key Considerations in Mold Design for Thin-Wall Injection Molding?
- 3. What are the Steps in the Thin-Wall Injection Molding Process?
- 4. What are the Three Key Factors in Mold Design for Thin-Wall Injection Molding?
- 5. What are the Applications of Thin-Wall Injection Molding?
- 6. What are the Differences Between Thin-Wall and Standard Injection Molding?
- 7. Conclusion
What is Thin-Wall Injection Molding?
Thin-wall injection molding is a process for creating plastic parts with very thin walls, typically less than 1mm thick, defined by a flow length to wall thickness ratio exceeding 200:1. It involves injecting molten plastic at high speed and pressure into molds with thin cavities, ensuring the material fills the mold before cooling. This technique is crucial for producing lightweight, cost-effective products like food containers, phone cases, and automotive components.
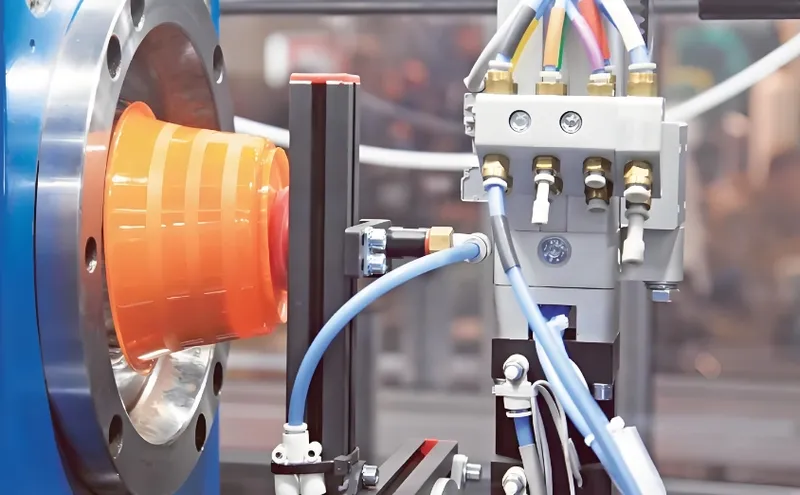
Thin-wall injection molding produces lightweight plastic parts4 with walls under 1mm, using high-speed injection5 to fill thin cavities, ideal for packaging, automotive, and electronics industries.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Wall Thickness | Typically <1mm, often 0.6-0.9mm |
| Flow Length Ratio | >200:1 |
| Key Challenges | Uniform filling, defect prevention |
| Common Materials | Polypropylene (PP), nylon (PA), polyethylene (PE) |
Core Principles
The process requires precise control over injection speed, pressure, and cooling to prevent defects like warping, sink marks, or short shots. Molds must be designed to handle high pressures and ensure even material distribution, making it more complex than standard injection molding.
Thin-wall injection molding is more cost-effective than standard injection molding.True
It reduces material usage and cycle times, leading to lower production costs for high-volume runs.
Thin-wall injection molding is unsuitable for all plastic materials.True
Only high-flow materials like polypropylene or nylon are suitable due to the need for rapid cavity filling.
What are the Key Considerations in Mold Design for Thin-Wall Injection Molding?
Designing molds for thin-wall injection molding requires attention to several critical factors to ensure part quality and process efficiency.
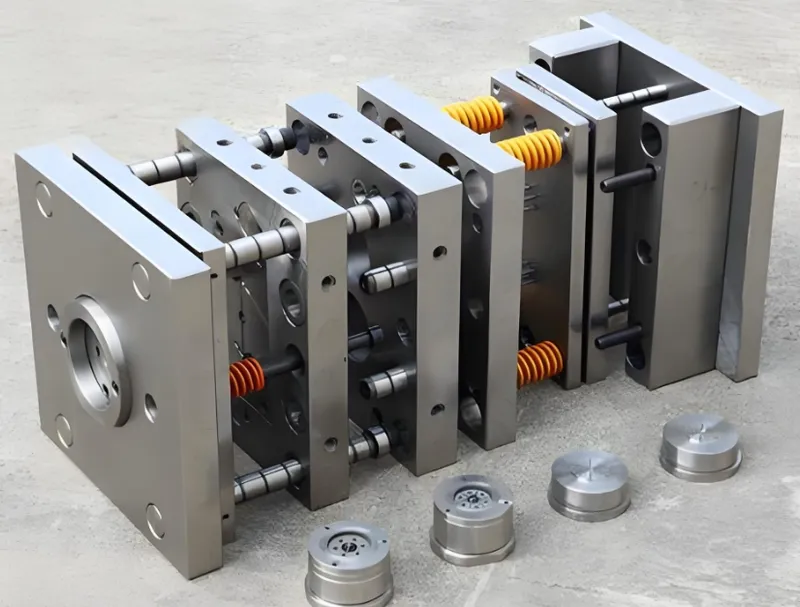

Key mold design considerations for thin-wall injection molding include uniform wall thickness, high-flow materials, precise gate placement, and efficient cooling and venting systems.
Uniform Wall Thickness
Maintaining consistent wall thickness is essential to prevent defects like warping or sink marks. For thin-wall parts, walls should be as uniform as possible, typically around 0.9mm or more, depending on the material and part size.
Material Selection
High-flow materials like polypropylene (PP), nylon (PA), and polyethylene (PE) are preferred because they can fill thin cavities quickly and evenly. These materials have a high melt flow index (MFI), which is crucial for thin-wall applications.

Gate Placement
Gates must be strategically placed to ensure even filling of the mold. For thin-wall parts, larger or multiple gates are often necessary to distribute the material uniformly and reduce the risk of short shots.
Cooling and Venting
Efficient cooling channels6 are vital to solidify the part quickly and maintain cycle times. Additionally, proper venting7 is required to prevent air traps, which can cause defects like burn marks or incomplete filling.
| Design Aspect | Recommendation | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Wall Thickness | ≥0.9mm, uniform | Prevents warping and sink marks |
| Material | High-flow plastics8 (e.g., PP, nylon) | Ensures proper cavity filling |
| Gate Placement | Multiple or larger gates | For even filling and reduced short shots |
| Cooling | Efficient channels | Quick solidification and cycle time control |
| Venting | Adequate vents | Avoids air traps and defects |
Uniform wall thickness is critical in thin-wall injection molding.True
It ensures even cooling and prevents defects like warping or sink marks.
Any plastic material can be used for thin-wall injection molding.False
Only materials with high flow rates are suitable for filling thin cavities effectively.
What are the Steps in the Thin-Wall Injection Molding Process?
The thin-wall injection molding process requires precise control at each stage to ensure high-quality parts and efficient production.
The thin-wall injection molding process involves material selection, mold design, high-speed injection, cooling, and quality control, with a focus on precision to avoid defects.

Material Selection
Choose high-flow materials like polypropylene or nylon to ensure the plastic can fill the thin cavities quickly and completely.
Mold Design
Design the mold with uniform wall thickness, optimized gate placement, and efficient cooling and venting systems to handle the high pressures and speeds involved.
Injection Process
Use high-speed injection machines (up to 2200 mm/s) and high pressure (≥200 MPa) to fill the mold rapidly before the material cools. This step is critical to avoid short shots or incomplete filling.
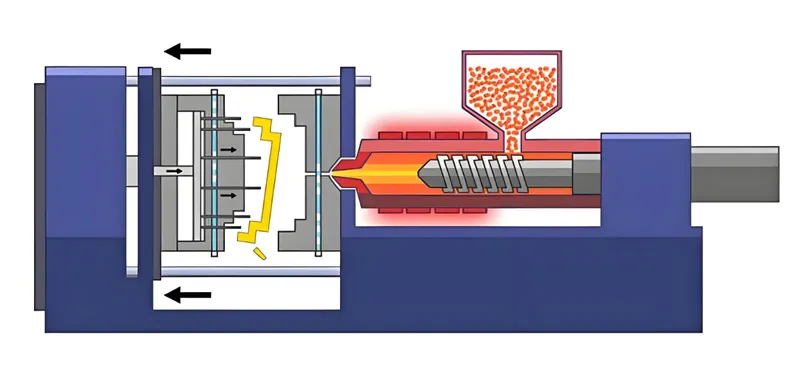
Cooling and Ejection
Cool the part quickly using well-designed cooling channels to solidify the material and maintain short cycle times. Eject the part carefully to avoid damage due to its thin walls.
Quality Control
Inspect parts for defects like sink marks, warping, or flow lines, ensuring they meet the required specifications.
High-speed injection is essential for thin-wall molding.True
It ensures the material fills the thin cavities before cooling, preventing defects.
Thin-wall injection molding always results in defect-free parts.False
Defects like warping or sink marks can still occur if mold design or process parameters are not optimized.
What are the Three Key Factors in Mold Design for Thin-Wall Injection Molding?
Effective mold design for thin-wall injection molding hinges on three critical factors that directly impact part quality and production efficiency.
The three key factors in mold design for thin-wall injection molding are wall thickness uniformity, gate design, and cooling efficiency, which together ensure defect-free parts and optimal cycle times.

Wall Thickness Uniformity
Uniform wall thickness prevents uneven cooling, which can lead to warping or sink marks. For thin-wall parts, maintaining consistency is even more critical due to the rapid cooling times.
Gate Design
Proper gate placement and size are essential for even material distribution. In thin-wall molding, multiple gates or larger gates are often used to ensure the material fills the entire cavity without hesitation.
Cooling Efficiency
Efficient cooling systems are necessary to solidify the part quickly and maintain short cycle times. Well-designed cooling channels help prevent defects and improve productivity.
Gate design is crucial for thin-wall injection molding.True
Proper gate placement ensures even filling and reduces the risk of defects like short shots.
Cooling efficiency is less important in thin-wall molding due to the thin walls.False
Efficient cooling is vital to prevent defects and maintain cycle times, even with thin walls.
What are the Applications of Thin-Wall Injection Molding?
Thin-wall injection molding is widely used in industries where lightweight, cost-effective parts are essential.
Thin-wall injection molding is commonly used in packaging, automotive, and consumer electronics for producing lightweight, cost-efficient parts like containers, interior trim, and phone cases.
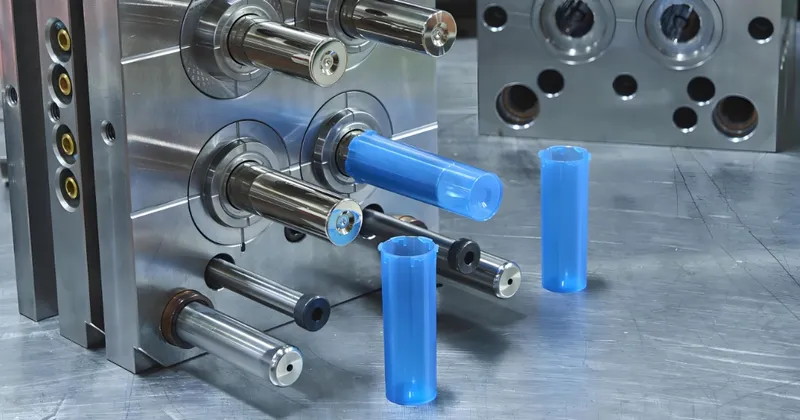
Packaging
Produces thin-walled containers, lids, and trays, reducing material costs and enhancing sustainability.
Automotive
Creates lightweight interior components like trim panels, contributing to improved fuel efficiency.

Consumer Electronics
Manufactures items like phone cases and battery covers, where thin walls allow for sleek designs and reduced weight.
Thin-wall injection molding is only used in the packaging industry.False
It is also widely used in automotive, electronics, and medical industries for lightweight components.
Thin-wall injection molding reduces production costs in high-volume manufacturing.True
It minimizes material usage and shortens cycle times, leading to significant cost savings.
What are the Differences Between Thin-Wall and Standard Injection Molding?
Understanding the differences between thin-wall and standard injection molding is key to selecting the right process for your application.
Thin-wall injection molding differs from standard injection molding in wall thickness, injection speed, pressure, and mold design, requiring specialized equipment and expertise.
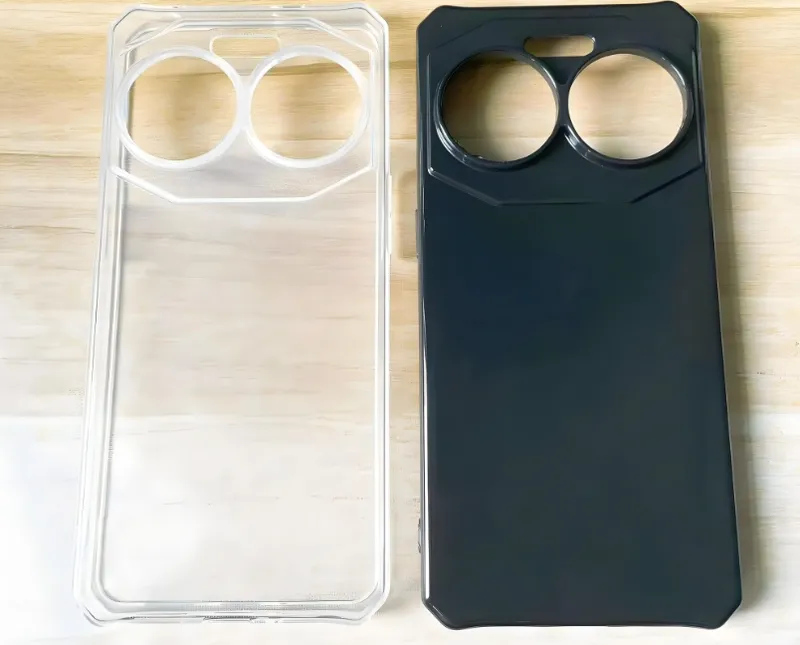

Wall Thickness
Thin-wall molding produces parts with walls typically less than 1mm, while standard molding handles thicker walls, usually above 1.5mm.
Injection Speed and Pressure
Thin-wall molding requires higher injection speeds (up to 2200 mm/s) and pressures (≥200 MPa) to fill molds quickly, whereas standard molding uses lower speeds and pressures.
Mold Design
Molds for thin-wall parts must be more robust, often made from harder steels like H-13 or D-2, to withstand higher pressures and prevent wear.
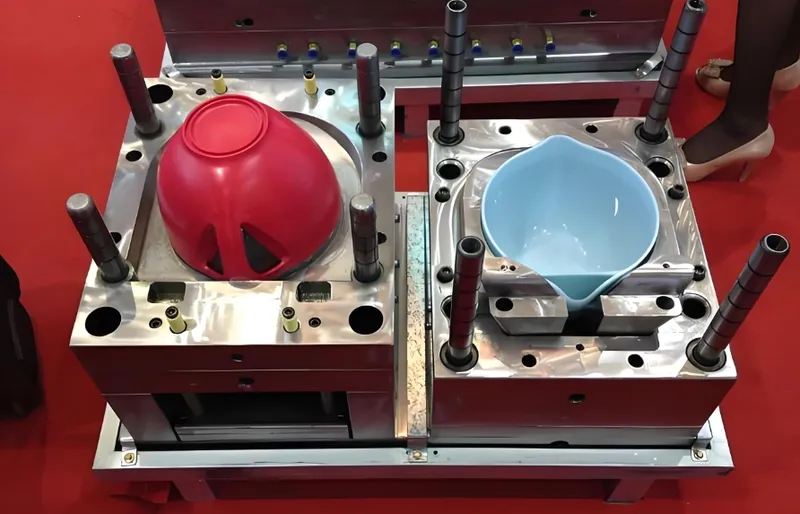
Cycle Times
Thin-wall molding generally has shorter cycle times due to faster cooling of thin parts, improving productivity.
Thin-wall injection molding requires more specialized equipment than standard molding.True
It demands high-speed machines and robust molds to handle the increased pressures and speeds.
Standard injection molding cannot produce thin-walled parts.False
While possible, it is less efficient and may not achieve the same quality as thin-wall-specific processes.
Conclusion
Thin-wall injection molding is a powerful process for producing lightweight, cost-effective plastic parts, but it requires careful mold design and process control. Key factors like uniform wall thickness, high-flow materials, and efficient cooling systems are essential for success. While more complex than standard molding, thin-wall injection molding offers significant benefits in material savings and production efficiency for the right applications.
Thin-wall injection molding is a cost-effective solution for high-volume production.True
It reduces material usage and cycle times, making it ideal for large-scale manufacturing.
Thin-wall injection molding is unsuitable for complex part designs.False
With proper mold design and process optimization, complex thin-wall parts can be successfully produced.
-
Discover the benefits and applications of thin-wall injection molding in various industries, enhancing your understanding of this efficient process. ↩
-
Learn about the critical aspects of mold design that ensure quality and efficiency in thin-wall injection molding, crucial for manufacturers. ↩
-
Explore how material selection affects the performance and cost-effectiveness of thin-wall injection molded parts, vital for successful production. ↩
-
Discover how lightweight plastic parts are manufactured and their advantages in modern applications. ↩
-
Learn about the significance of high-speed injection in molding processes and its impact on product quality. ↩
-
Understanding efficient cooling channels can enhance your production process and reduce defects. ↩
-
Exploring proper venting techniques can help you avoid defects and improve product quality. ↩
-
Learning about high-flow plastics can guide material selection for better performance in your projects. ↩






