Applying Lean Manufacturing1 principles to injection molding optimizes production by eliminating waste2, reducing costs, and improving efficiency, making it ideal for industries like automotive and consumer goods.
Lean Manufacturing enhances injection molding by streamlining processes, cutting waste, and boosting productivity3, offering significant benefits for high-volume manufacturing.
Understanding how Lean principles integrate with injection molding can transform your production strategy. Dive into this guide to explore how these methodologies work together to deliver high-quality parts efficiently.
Lean Manufacturing reduces production costs in injection molding.True
By minimizing waste such as excess inventory and defects, Lean lowers material and operational costs.
Lean principles are only applicable to large-scale manufacturers.False
Lean can benefit businesses of all sizes by improving efficiency, though implementation may vary based on scale.
- 1. What is Lean Manufacturing in Injection Molding?
- 2. What are the Steps in the Injection Molding Process with Lean?
- 3. What are the Key Factors in Applying Lean to Injection Molding?
- 4. What are the Applications of Lean in Injection Molding?
- 5. What are the Differences Between Lean and Traditional Injection Molding?
- 6. Conclusion
What is Lean Manufacturing in Injection Molding?
Lean Manufacturing is a methodology focused on eliminating waste—anything that doesn’t add value to the final product—while enhancing productivity and quality. In injection molding, a process where molten material is injected into molds to create precise parts, Lean principles streamline operations to make them faster, cheaper, and more reliable.

Lean Manufacturing4 in injection molding eliminates waste, reduces cycle times, and improves part quality, benefiting industries like automotive, medical, and consumer goods.
| Lean Principle | Application in Injection Molding | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Just-In-Time (JIT)5 | Produce only what’s needed | Reduces inventory costs |
| 5S Methodology6 | Organize workspace | Increases efficiency |
| Kaizen | Continuous improvement | Enhances process quality |
Lean Manufacturing
Originating from the Toyota Production System, Lean emphasizes efficiency through waste reduction. In injection molding, it targets seven wastes: waiting, inventory, transportation, motion, overprocessing, overproduction, and defects. For example, reducing idle machine time or excess material use directly improves profitability (Lean Manufacturing Processes).
Injection Molding
Injection molding involves injecting molten materials—typically thermoplastics like ABS or polypropylene—into a mold to form parts. It’s widely used for its precision and scalability. Lean enhances this by optimizing each step, from material selection to ejection (Plastic Injection Molding).
Lean Manufacturing improves injection molding efficiency.True
By streamlining workflows and reducing downtime, Lean boosts throughput and resource use.
Injection molding cannot benefit from Lean without automation.False
While automation helps, Lean improvements like 5S and JIT can be applied manually with significant results.
What are the Steps in the Injection Molding Process with Lean?
The injection molding process7, when paired with Lean principles, becomes a highly efficient system for producing quality parts with minimal waste.
Lean principles8 optimize the injection molding process—clamping, injection, cooling, and ejection—by reducing waste and improving cycle times.

Clamping
The mold is closed and secured. Lean applies quick-change tooling to cut setup times, ensuring faster transitions between production runs.
Injection
Molten material is injected into the mold. Lean optimizes parameters like pressure and speed to reduce material waste and defects.
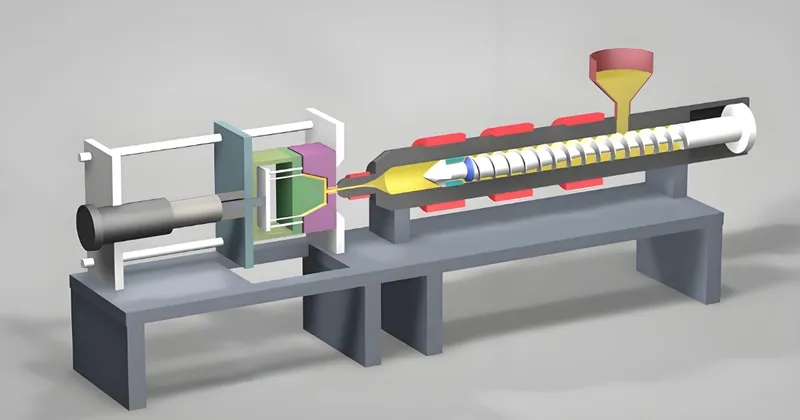
Cooling
The material solidifies. Lean balances cooling time with cycle efficiency, using advanced techniques like conformal cooling9 to maintain quality.
Ejection
The part is removed from the mold. Lean ensures smooth ejection through smart design, minimizing damage and rework.
Lean reduces cycle times in injection molding.True
Optimizing setup and process steps shortens production cycles without sacrificing quality.
Lean eliminates all defects in injection molding.False
While Lean reduces defects significantly, some variability may persist due to material or equipment factors.
What are the Key Factors in Applying Lean to Injection Molding?
Applying Lean to injection molding hinges on process optimization, workforce training, and material selection to maximize efficiency and quality.
Lean in injection molding depends on process efficiency, employee training, and material compatibility to achieve waste reduction and cost savings.

Process Efficiency
Lean tools like 5S and Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) keep machines running smoothly and workspaces organized, reducing downtime and boosting output (Lean Principles).
Employee Training
Lean requires a cultural shift. Comprehensive training on principles like Kaizen ensures staff can identify and eliminate waste, though resistance to change can be a hurdle.

Material Compatibility
Choosing materials with optimal flow and minimal shrinkage—like thermoplastics—enhances Lean outcomes by reducing scrap and rework (Material Selection).
Training is essential for Lean success in injection molding.True
Well-trained staff can effectively implement Lean strategies, driving continuous improvement.
Lean works equally well with all materials.False
Material properties affect Lean outcomes; some require more adjustments to minimize waste.
What are the Applications of Lean in Injection Molding?
Lean Manufacturing in injection molding supports a wide range of industries by delivering efficient, high-quality production tailored to specific needs.
Lean injection molding is applied in automotive, consumer goods, and medical industries for cost-effective, high-volume part production.

Automotive Industry
Lean reduces cycle times and ensures consistent quality for parts like dashboards and bumpers, critical for assembly lines (Lean Goals).
Consumer Goods
JIT production minimizes inventory, meeting demand fluctuations for items like appliance housings and toys.

Medical Devices
Lean enhances quality control for components like syringes, reducing defects in critical applications.
Lean improves competitiveness in injection molding.True
Lower costs and higher quality give manufacturers an edge in global markets.
Lean is only useful for high-volume production.False
Lean benefits low-volume runs too, by reducing waste and improving flexibility.
What are the Differences Between Lean and Traditional Injection Molding?
Process Approach
Traditional molding focuses on output, often tolerating inefficiencies. Lean prioritizes value, systematically cutting waste at every step.

Efficiency
Lean shortens cycle times and reduces resource use, while traditional methods may involve longer setups and higher scrap rates.
Cost Impact
Lean lowers costs through waste reduction; traditional molding may incur higher expenses due to overproduction or defects (Lean Benefits).

Conclusion
Applying Lean Manufacturing to injection molding revolutionizes production by eliminating waste, enhancing quality, and reducing costs. From automotive to medical applications, Lean delivers efficient, scalable solutions. Start with small steps—organize your workspace with 5S, train your team, and optimize processes—to unlock its full potential (Lean Implementation).
-
Explore how Lean Manufacturing can revolutionize your injection molding processes and enhance efficiency. ↩
-
Learn about the critical role of waste elimination in optimizing injection molding and increasing profitability. ↩
-
Discover effective strategies to enhance productivity in injection molding through Lean principles for better outcomes. ↩
-
Explore how Lean Manufacturing can transform injection molding processes, enhancing efficiency and quality in production. ↩
-
Learn about the Just-In-Time (JIT) approach and its significant impact on reducing costs and improving inventory management. ↩
-
Discover the 5S Methodology and its role in organizing workspaces for maximum efficiency and productivity. ↩
-
Exploring the injection molding process will provide insights into its efficiency and applications in various industries. ↩
-
Understanding Lean principles can enhance your knowledge of efficient manufacturing processes and waste reduction strategies. ↩
-
Learning about conformal cooling can help you understand advanced techniques that improve the efficiency and quality of molded parts. ↩






