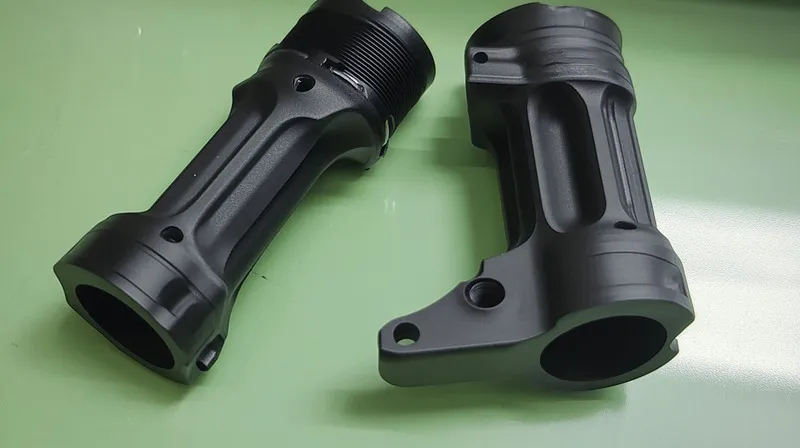
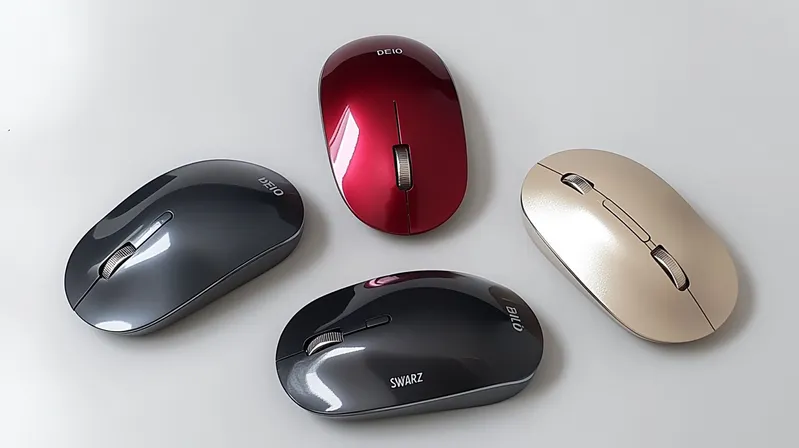
The high-gloss injection molding1 process creates premium, shiny plastic parts by using polished molds and specific materials, enhancing aesthetics and durability for various industries.
High-gloss injection molding uses polished molds2 and materials like ABS or polycarbonate to produce reflective surfaces3, ideal for consumer electronics, automotive interiors, and more.
Understanding the nuances of high-gloss injection molding can elevate your product’s appeal. Dive in to learn how mold quality, material choice, and process control combine to achieve that flawless, mirror-like finish.
High-gloss injection molding reduces manufacturing costs.False
While it enhances aesthetics, high-gloss molding increases costs due to specialized molds and precise control requirements.
High-gloss finishes are only for consumer electronics.False
Beyond electronics, high-gloss finishes are used in automotive, household appliances, and medical devices for their premium look and durability.
- 1. What are the Common Materials Used in High-Gloss Injection Molding?
- 2. What are the Steps in the High-Gloss Injection Molding Process?
- 3. What are the Three Key Factors in Achieving a High-Gloss Finish?
- 4. What are the Applications of High-Gloss Injection Molding?
- 5. What are the Differences Between High-Gloss and Standard Injection Molding?
- 6. Conclusion
What are the Common Materials Used in High-Gloss Injection Molding?
Material selection is critical in high-gloss injection molding, determining the part’s shine, durability, and suitability for specific applications.
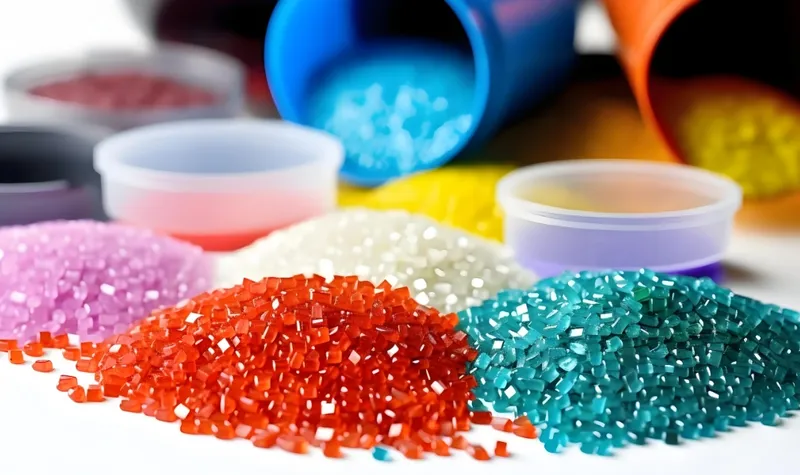

Common materials include ABS, polycarbonate, PMMA, and polystyrene, chosen for their ability to produce smooth, reflective surfaces4.
| Material Type | Recommended Max Thickness | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| General Thermoplastics5 | 3 – 4 mm | Ensures uniform cooling |
| High-strength Plastics | Up to 8 mm | Requires careful design |
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
ABS excels in high-gloss molding due to its moldability and smooth finish. It’s a go-to for electronics (think TV panels) and automotive parts (like dashboards). Brands like LG and Ford rely on ABS for its consistent shine.
Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate delivers transparency and gloss with the right additives, perfect for lenses or headlights. Its toughness and clarity make it a favorite in automotive and optical applications. Check out Polycarbonate’s properties for more.

Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
PMMA, or acrylic, offers optical clarity and a glossy surface, ideal for displays and light covers. Its light transmission paired with shine suits electronics and automotive uses perfectly.
Polystyrene (PS)
Polystyrene provides a cost-effective glossy finish for simpler items like toys or containers. Its ease of processing makes it a practical choice for mass production.
ABS is a key material for high-gloss molding.True
ABS’s moldability and smooth finish make it a staple in high-gloss applications.
Any plastic can achieve a high-gloss finish.False
Only specific plastics like ABS, PC, PMMA, and PS have the properties needed for high-gloss finishes.
What are the Steps in the High-Gloss Injection Molding Process?
The process demands precision at every stage to ensure a flawless, shiny outcome.
High-gloss injection molding involves mold prep, material selection, injection, cooling, and ejection, all optimized for a reflective finish.

Mold Design and Preparation
Start with a mold polished to SPI-A1, A2, or A3 standards6 using diamond buffing. Uniform wall thickness prevents warping, and piping enables rapid heating/cooling.
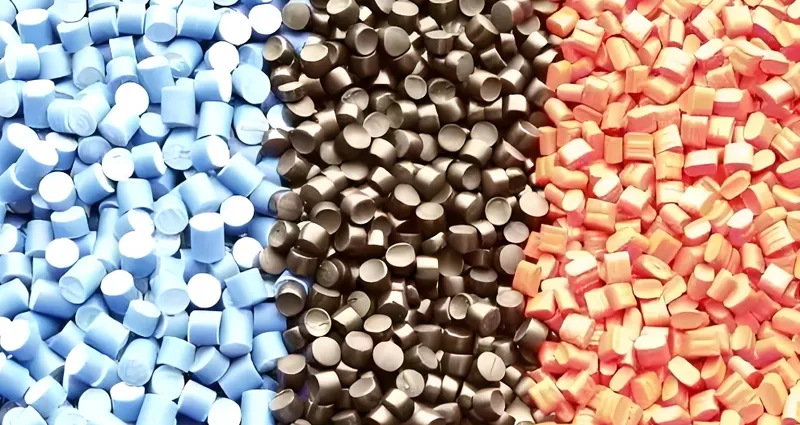
Material Selection
Pick thermoplastics like ABS, PC, PMMA, or PS7 for gloss potential. Additives can boost shine without sacrificing strength.
Injection Molding
Melt the plastic and inject it at 180°C–200°C with high pressure to fill the mold perfectly. Temperature control avoids defects like flow marks.
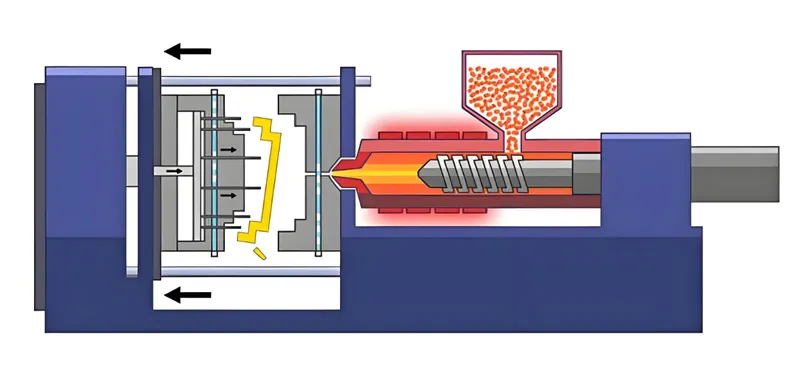
Cooling
Cool rapidly and uniformly with cold water and air to lock in the gloss. This step prevents warping and ensures surface quality.
Ejection and Finishing
Eject gently to avoid scratches. If optimized, little post-finishing is needed—just careful touch-ups if required.
High-gloss molding always yields a perfect finish.False
Success hinges on mold quality, material, and process precision.
Temperature control is critical for gloss.True
It affects flow and cooling, directly impacting surface quality.
What are the Three Key Factors in Achieving a High-Gloss Finish?
Success in high-gloss molding boils down to three essentials.
Mold surface quality, material selection, and process parameters (temperature, pressure, cooling) are the keys to a high-gloss finish.

Mold Surface Quality
A mirror-like mold (SPI-A1, A2, or A3) is non-negotiable. Diamond buffing ensures no imperfections transfer to the part.
Material Selection
Choose ABS, PC, PMMA, or PS for their gloss-friendly properties. Flow characteristics and additives matter too.

Process Parameters
-
Temperature: 180°C–200°C for optimal flow; over 220°C risks degradation.
-
Pressure: High enough to fill the mold without gaps.
-
Cooling: Fast and even to set the shine and shape.
Mold quality trumps all for gloss.True
A polished mold is the foundation of a mirror-like finish.
Any machine can do high-gloss molding.False
It requires specialized equipment and tight control.
What are the Applications of High-Gloss Injection Molding?
High-gloss finishes shine in industries valuing looks and longevity.
Used in electronics, automotive, appliances, and medical devices, high-gloss molding enhances appeal and durability.

Consumer Electronics
TV panels, monitors, and phone cases get a premium boost8. Samsung and Apple leverage this for flagship products.
Automotive
Dashboards and trim gain a luxe feel9. BMW and Mercedes-Benz use it for interiors that impress.

Household Appliances
Handles and panels (e.g., Dyson vacuums) combine style and cleanability with gloss.
Medical Devices
Visible parts benefit from hygiene and aesthetics, thanks to smooth, glossy surfaces.
Gloss is just for looks.False
It also adds durability and ease of cleaning.
Gloss molding suits small runs.False
High costs favor large-scale production.
What are the Differences Between High-Gloss and Standard Injection Molding?
Mold Preparation
High-gloss needs SPI-A1/A2/A3 polished molds; standard can use textured or less polished ones.
Material Selection
Gloss limits you to ABS, PC, PMMA, PS; standard molding handles more plastics.
Process Control
Gloss demands precision in temperature, pressure, and cooling; standard is more forgiving.
Cost
Gloss costs more due to molds and equipment; standard is cheaper overall.

Applications
Gloss targets premium aesthetics; standard fits broader uses.
Conclusion
High-gloss injection molding blends art and science to craft standout plastic parts. Master mold prep, material choice, and process control, and you’ll deliver products that dazzle. It’s pricier and trickier, but for premium goods, the payoff’s worth it. Consult experts to nail it.
-
Explore this link to understand how high-gloss injection molding can enhance product aesthetics and durability, making it essential for various industries. ↩
-
Discover the significance of polished molds in achieving superior finishes in injection molding, crucial for high-quality production. ↩
-
Learn about the diverse applications of reflective surfaces in manufacturing, which can significantly impact product design and functionality. ↩
-
Exploring techniques for achieving smooth surfaces can improve your manufacturing processes and product aesthetics. ↩
-
Learning about General Thermoplastics will help you make informed decisions on material selection for your projects. ↩
-
Learn about SPI standards in mold polishing to ensure quality and precision in your manufacturing process. ↩
-
Discover the best thermoplastics for achieving high-gloss finishes and their properties to enhance your projects. ↩
-
Discover insights on how a premium boost can influence consumer choices and brand loyalty in electronics. ↩
-
Learn how a luxe feel in automotive design can elevate brand perception and customer satisfaction. ↩





