Die casting and injection molding1 are two powerhouse manufacturing processes that shape the world around us, from the cars we drive to the gadgets we use daily. But what sets them apart? In this deep dive, we’ll explore the key differences between die casting and injection molding, helping you understand which process might be best for your next project.
Die casting uses molten metal to create strong, precise parts, while injection molding uses molten plastic for lightweight, versatile components. Both excel in producing complex shapes but cater to different materials and applications.
Understanding when to use die casting2 versus injection molding can save time, reduce costs, and ensure your product meets its performance requirements. Let’s explore the nuances of each process.
Die casting is only used for small parts.False
Die casting can produce both small and large parts, though it’s more common for smaller, intricate components like engine parts and hardware.
Injection molding is less precise than die casting.False
Both processes offer high precision, but die casting is often preferred for metal parts requiring tighter tolerances.
- 1. What Are the Common Materials Used in Die Casting and Injection Molding?
- 2. What Are the Steps in the Die Casting and Injection Molding Processes?
- 3. What Are the Applications of Die Casting and Injection Molding?
- 4. What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Die Casting and Injection Molding?
- 5. How to Choose Between Die Casting and Injection Molding?
- 6. Conclusion
What Are the Common Materials Used in Die Casting and Injection Molding?
Materials play a pivotal role in determining which process to use, as die casting and injection molding cater to entirely different material families.

Die casting typically uses non-ferrous metals like aluminum, zinc, and magnesium, while injection molding works with thermoplastics3 such as ABS, polycarbonate, and nylon.
| Process | Common Materials | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Die Casting | Aluminum, Zinc, Magnesium, Copper alloys | High strength, durability, heat resistance |
| Injection Molding | ABS, Polycarbonate, Polypropylene, Nylon | Lightweight, versatile, corrosion-resistant |
Die Casting Materials
In die casting, the stars of the show are metals like aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. These materials offer exceptional strength and durability, making them ideal for parts that need to withstand tough conditions. For example, aluminum is lightweight yet strong, perfect for automotive components, while zinc provides excellent corrosion resistance for hardware.
Injection Molding Materials
Injection molding works its magic with plastics such as ABS, polycarbonate, and nylon. These materials are lightweight, versatile, and can be engineered for specific properties like flexibility or heat resistance. ABS, for instance, is known for its impact resistance, making it a go-to for consumer electronics.
Die casting can be used with plastics.False
Die casting is specifically designed for metals, while injection molding is for plastics.
Injection molding materials are always weaker than die casting materials.False
While metals generally offer higher strength, advanced plastics can provide comparable performance in certain applications.
What Are the Steps in the Die Casting and Injection Molding Processes?
Both processes follow a similar sequence—melting the material4, injecting it into a mold, cooling, and ejecting the part—but the details differ significantly due to the materials involved.
Die casting involves melting metal, injecting it under high pressure into a mold, cooling, and ejecting the part. Injection molding follows a similar process but uses molten plastic at lower temperatures and pressures.
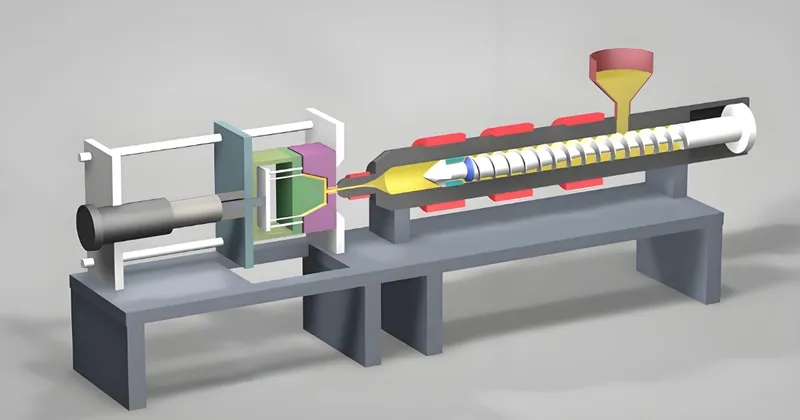
Die Casting Process Steps
-
Melting the Metal: Metals like aluminum or zinc are melted in a furnace at high temperatures (e.g., 600-700°C for aluminum).
-
Injection: The molten metal is injected into a steel mold under high pressure (15-100 MPa).
-
Cooling: The metal cools and solidifies quickly, often within seconds.

- Ejection: The mold opens, and the part is ejected, ready for finishing if needed.
Injection Molding Process Steps
-
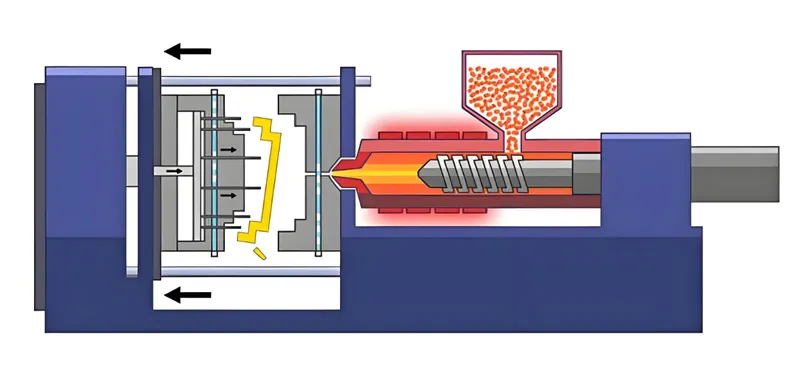
Melting the Plastic: Plastic pellets are melted in a barrel at lower temperatures (e.g., 200-300°C for ABS).
-
Injection: The molten plastic is injected into a mold under pressure.
-
Cooling: The plastic cools and solidifies, typically taking a few seconds to minutes.
-
Ejection: The mold opens, and the part is ejected, often requiring little to no finishing.
Die casting requires higher temperatures than injection molding.True
Metals have higher melting points than plastics, necessitating higher temperatures in die casting.
Both processes use the same type of molds.False
Die casting uses steel molds to withstand high pressures and temperatures, while injection molding can use aluminum or steel molds depending on production volume.
What Are the Applications of Die Casting and Injection Molding?
The choice between die casting and injection molding often comes down to the specific requirements of the application, as each process excels in different industries.
Die casting is ideal for automotive parts, hardware, and electronics housings, while injection molding is preferred for consumer goods, medical devices, and toys.

Die Casting Applications
Die casting shines in the automotive industry5, producing engine components, transmission housings, and even door handles. It’s also a go-to for hardware like locks and hinges, as well as electronics housings that require durability and precision.

Injection Molding Applications
Injection molding is the backbone of consumer goods, from Lego bricks to smartphone cases. It’s also indispensable in the medical field for items like syringes and surgical tools, where precision and material versatility are key.
Die casting is only used in the automotive industry.False
While common in automotive, die casting is also used in electronics, hardware, and industrial equipment.
Injection molding is unsuitable for high-strength applications.False
Advanced plastics and reinforced composites can provide high strength for demanding applications.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Die Casting and Injection Molding?
Both processes offer unique benefits and drawbacks, making them suitable for different scenarios.

Die casting provides high strength and precision for metal parts but comes with higher tooling costs. Injection molding offers material versatility and lower per-unit costs for large runs but may not match the strength of metal parts.
| Aspect | Die Casting | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | High (metal parts) | Varies (plastic parts) |
| Complexity | Excellent for intricate designs | Also great for complex shapes |
| Tooling Cost | Higher (steel molds) | Lower (aluminum or steel molds) |
| Production Speed | Fast once set up | Very fast for high-volume production |
| Material Cost | Higher (metals) | Lower (plastics) |
Die Casting: Pros and Cons
- Pros: High strength, excellent dimensional accuracy, suitable for complex shapes, and fast production rates.

- Cons: Limited to non-ferrous metals, high initial tooling costs, and less suitable for very large parts.
Injection Molding: Pros and Cons
- Pros: Wide range of material choices, ability to produce large and small parts, high production rates, and cost-effective for large volumes.

- Cons: High initial tooling costs for small runs, potential strength limitations compared to metals, and challenges with dimensional stability for large parts.
Die casting is always more expensive than injection molding.False
Costs depend on production volume, material, and part complexity. For large runs, injection molding can be more cost-effective.
Injection molding cannot produce parts with tight tolerances.False
Injection molding can achieve tight tolerances, especially with advanced techniques and materials.
How to Choose Between Die Casting and Injection Molding?
Selecting the right process depends on several factors, including material requirements, production volume, and budget.
Choose die casting for metal parts requiring high strength and precision; opt for injection molding for plastic parts in high-volume production with versatile material options.

Consider these factors:
-
Material: Need metal strength? Go with die casting. Need plastic versatility? Choose injection molding.
-
Production Volume6: For massive quantities, injection molding often wins on cost due to lower per-unit expenses.

-
Part Complexity: Both processes handle intricate designs, but die casting may have an edge for very thin walls in metal parts.
-
Budget: Die casting typically has higher upfront tooling costs, but per-unit costs can be competitive for certain projects.
Die casting is better for all types of parts.False
Die casting is ideal for metal parts, but injection molding is better for plastic components and high-volume production.
Injection molding is always faster than die casting.False
Production speed depends on part size, complexity, and setup time. Both can be fast once production begins.
Conclusion
Both die casting and injection molding are invaluable tools in the manufacturing toolbox7, each with its strengths and ideal use cases. Die casting excels in producing strong, precise metal parts for industries like automotive and electronics, while injection molding offers unmatched versatility and cost-efficiency for plastic components in consumer goods and medical devices.
By understanding their differences—from materials and process steps to applications and costs—you can make informed decisions that bring your designs to life efficiently and effectively.
-
Discover the advantages of injection molding and how it can be applied in various industries by visiting this resource. ↩
-
Explore this link to gain a deeper understanding of die casting, its applications, and benefits in manufacturing. ↩
-
Learn about thermoplastics, their properties, and applications in manufacturing processes like injection molding by checking this link. ↩
-
Learn about the differences in material melting processes between die casting and injection molding for better manufacturing insights. ↩
-
Stay updated on the automotive industry’s trends and how manufacturing processes like Die casting are evolving. ↩
-
Learn how production volume impacts manufacturing choices, ensuring you select the best method for your project’s scale and budget. ↩
-
Discover the essential tools in manufacturing, including die casting and injection molding, to enhance your production knowledge. ↩




