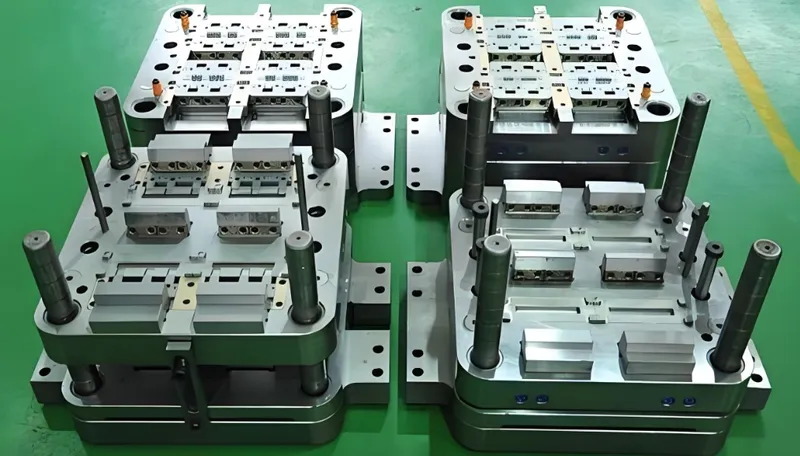
In the world of injection molding, efficiency is everything. Manufacturers constantly seek ways to produce more parts in less time without compromising quality. Enter multi-cavity molds1—these specialized tools allow the creation of multiple identical parts in a single cycle, slashing production times2 and costs. But designing them isn’t a walk in the park; it demands precision and foresight.
Multi-cavity molds produce multiple identical parts per cycle, boosting efficiency and cutting costs, but require meticulous design3 to ensure uniform quality across all cavities.
This guide unpacks the essentials of multi-cavity mold design, from core principles to practical applications. Whether you’re weighing them against other mold types or diving into the technical details, you’ll find actionable insights here.
Multi-cavity molds are always more cost-effective than single-cavity molds.False
While they lower per-part costs in high-volume runs, their higher upfront costs make them less ideal for small batches.
Multi-cavity molds are only for small, simple parts.False
They can handle complex parts, though design complexity increases accordingly.
- 1. What Are Multi-Cavity Molds?
- 2. What Are the Typical Applications of Multi-Cavity Molds?
- 3. What Are the Key Steps in Designing Multi-Cavity Molds?
- 4. What Are the Essential Design Considerations for Multi-Cavity Molds?
- 5. What Are the Related Technologies in Multi-Cavity Mold Design?
- 6. Conclusion
What Are Multi-Cavity Molds?
Multi-cavity molds are the backbone of high-volume injection molding4, enabling manufacturers to churn out identical parts swiftly and economically.
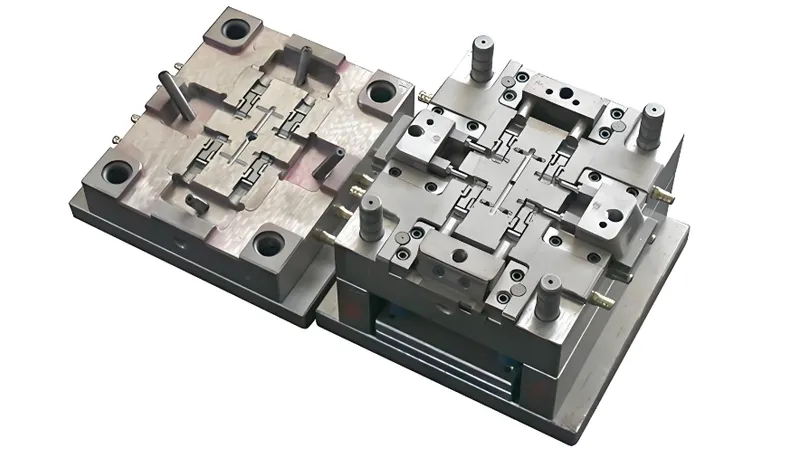
Multi-cavity molds feature multiple identical cavities in a single tool, producing several parts per cycle, perfect for industries like automotive, medical, and consumer goods.
| Mold Type | Cavities | Production Volume | Initial Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Cavity | 1 | Low to Medium | Low |
| Multi-Cavity | 2+ | High | High |
| Family Mold | Multiple (different parts) | Medium | Medium to High |
Definition and Core Principles
A multi-cavity mold is an injection molding tool with multiple identical cavities, each crafting the same part simultaneously (Protolabs). Unlike single-cavity molds, which yield one part per cycle, or family molds, which produce varied parts, multi-cavity molds prioritize uniformity and speed. The key? Balanced material flow, cooling, and ejection across all cavities to ensure consistent quality.
Classification of Multi-Cavity Molds
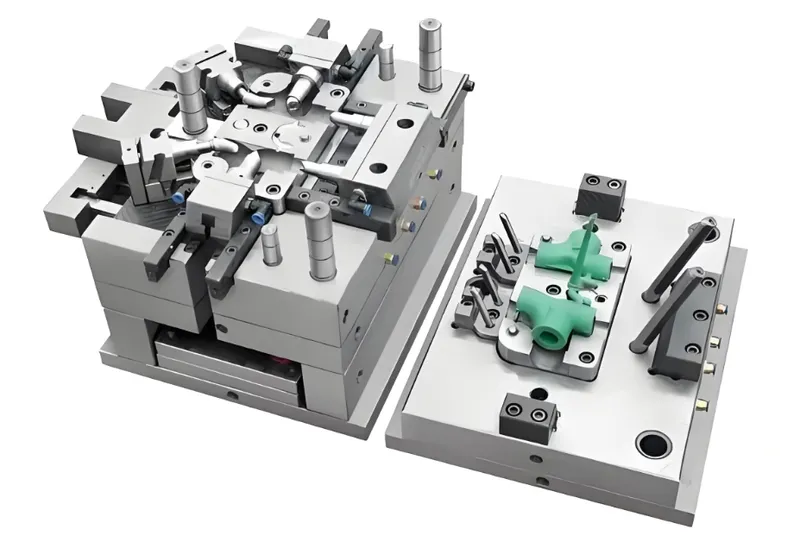
Multi-cavity molds vary by:
-
Number of Cavities: From 2 to 128, depending on part size (e.g., 16 for bottle caps) (SyBridge Technologies).
-
Process: Predominantly injection molding for plastics.
-
Application: Used in packaging, automotive clips, and medical syringe parts.
| Classification Type | Examples | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Cavities | 4-cavity, 16-cavity | Bottle caps, automotive clips |
| Process | Injection molding | High-volume plastic parts |
| Application | Consumer goods, medical | Packaging, diagnostic devices |
Multi-cavity molds guarantee identical parts across all cavities.False
Uniformity depends on precise design; imbalances can cause variations.
What Are the Typical Applications of Multi-Cavity Molds?
Multi-cavity molds shine in scenarios demanding high output of identical parts, offering both speed and savings.
Multi-cavity molds excel in automotive, medical, and consumer goods sectors, producing parts like clips, syringe components, and bottle caps in bulk.
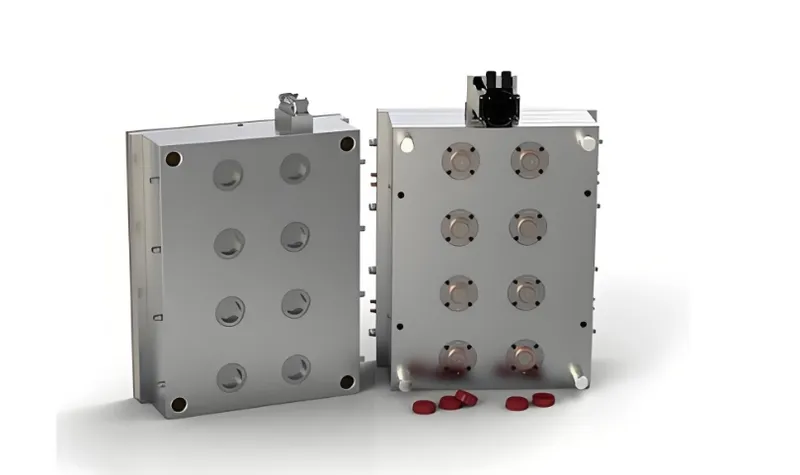
Industry-Specific Applications
-
Automotive: Clips, connectors, interior parts (3ERP).
-
Medical: Syringe barrels, diagnostic components.

-
Consumer Goods: Bottle caps, containers.
-
Packaging: High-cavity molds (up to 128) for lids and closures.
Pros and Cons Comparison
| Mold Type | Pros | Cons | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Cavity5 | High output, low per-part cost | High initial cost, complex design | High-volume identical parts |
| Single-Cavity6 | Low cost, simple design | Slow production, high per-part cost | Prototyping, low-volume |
| Family Mold7 | Multiple parts per cycle | Complex, higher defect risk | Related parts for assemblies |
Multi-cavity molds reduce production time significantly.True
Producing multiple parts per cycle shortens lead times for large orders.
What Are the Key Steps in Designing Multi-Cavity Molds?
Designing a multi-cavity mold is a technical endeavor that hinges on precision to deliver flawless parts.
The design process involves initial prototyping, mold flow simulation, runner and gate design, thermal management, and testing to ensure balanced performance.
Design Workflow Breakdown
-
Initial Design: Test with a single-cavity mold to validate part geometry.
-
Mold Flow Simulation: Use tools like MoldFlow to predict filling and cooling (MoldMaking Technology).
-
Runner and Gate Design: Opt for balanced “H” runners and strategic gates (FOW Mould).
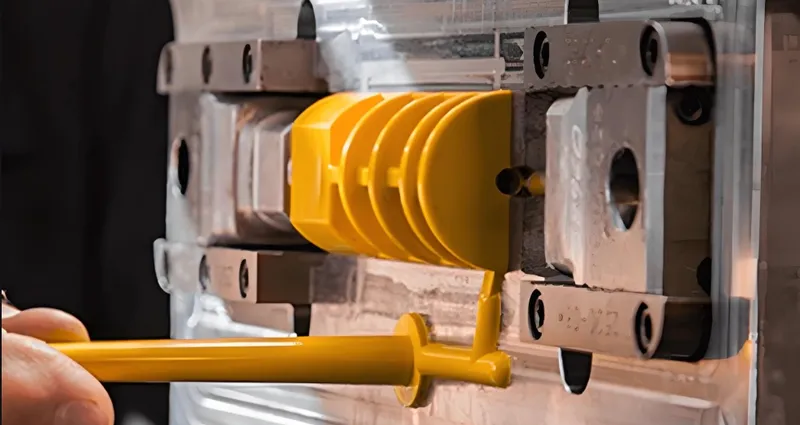

-
Thermal Management: Add cooling channels for even heat dissipation.
-
Material Selection: Pick materials with optimal flow for multi-cavity setups.
-
Validation: Test and tweak for consistency.
Material Compatibility
- Flow: High-viscosity materials need larger gates (Kaso Plastics).

-
Thermal: Cooling rates influence cycle times.
-
Impact: Wrong choices lead to defects like uneven filling.
All cavities fill at the same rate.False
Balanced runners are critical for uniform filling.
What Are the Essential Design Considerations for Multi-Cavity Molds?
Success in multi-cavity mold design rests on addressing key factors to maintain efficiency and quality.
Critical considerations include cavity layout, runner balance, cooling uniformity, gate precision, and material choice for consistent results.
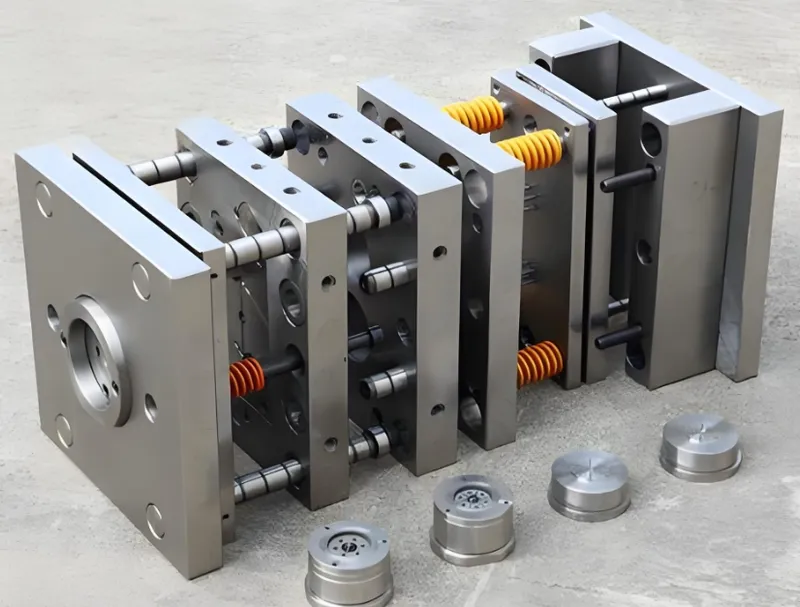

Design Checklist
-
Part Design: Avoid complex undercuts; ensure uniform wall thickness.
-
Mold Flow: Simulate to catch defects early.
-
Gates: Position for balanced filling (e.g., tab gates).
-
Runners: Use “H” shapes or hot runners for large molds.
-
Cooling: Design uniform channels.
-
Material: Match flow and thermal properties to mold.
-
Ejection: Plan for smooth, damage-free removal.
-
Maintenance: Enable easy cavity access.
-
Cost: Weigh initial investment vs. per-part savings.
-
Volume: Justify with high demand (e.g., >10,000 units).
Process Selection Decision-Making
| Decision Factor | Multi-Cavity Mold | Single-Cavity Mold | Family Mold |
|---|---|---|---|
| Production Volume | High (>10,000 units) | Low (<10,000 units) | Medium, assemblies |
| Part Complexity | Simple, identical | Complex or prototype | Varied parts |
| Initial Cost | High | Low | Medium to high |
| Per-Part Cost | Low | High | Medium |
Hot runner systems are essential for all multi-cavity molds.False
They’re useful for large molds but not mandatory for smaller ones.
Multi-cavity molds integrate with cutting-edge tools to streamline design and production.
Technologies like CAD/CAM, mold flow simulation, hot runners, and automation enhance multi-cavity mold efficiency and precision.
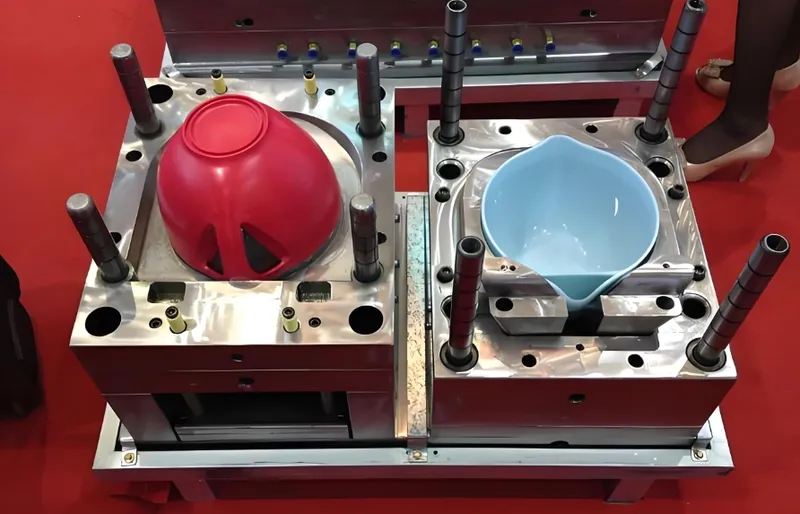
Key Technologies
-
CAD/CAM: Software like SolidWorks for detailed design.
-
Mold Flow Simulation: Optimizes filling and cooling.
-
Hot Runners: Reduce waste in large molds (SyBridge Technologies).
-
Automation: Robotics for part handling (Star Rapid).
| Technology Type | Examples | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Upstream | CAD/CAM | Design optimization |
| Downstream | Automation | Post-molding efficiency |
| Complementary | Hot Runners | Waste reduction |
CAD software is optional in multi-cavity mold design.False
It’s vital for precision and simulation.
Conclusion
Multi-cavity molds are a powerhouse for high-volume production, cutting costs and time while demanding careful design. From balanced flow to uniform cooling, every detail matters. They’re a top pick for industries like automotive and medical but shine brightest in large runs of simple parts. For smaller batches or complex designs, alternatives might edge them out.
-
Explore the advantages of multi-cavity molds to enhance your production efficiency and reduce costs effectively. ↩
-
Learn strategies to minimize production times in injection molding, ensuring faster turnaround and increased productivity. ↩
-
Discover best practices for meticulous design in mold making to ensure high-quality and efficient production processes. ↩
-
Learn about high-volume injection molding processes to see how they optimize production and reduce costs for manufacturers. ↩
-
Explore the benefits of Multi-Cavity molds to understand how they can enhance production efficiency and reduce costs. ↩
-
Learn about the limitations of Single-Cavity molds to make informed decisions for your manufacturing needs. ↩
-
Discover how Family Molds can optimize production for related parts and improve assembly efficiency. ↩





