Injection molding machines can produce both PPR and PVC fittings1 with proper adjustments, but the distinct properties of each material necessitate specific temperature settings, cleaning protocols, and maintenance to ensure quality and machine longevity.
Understanding these nuances is essential for manufacturers aiming to leverage injection molding’s versatility. Let’s dive into the details, from material definitions to technical processes and practical applications.
Injection molding machines can produce both PPR and PVC fittings.True
With appropriate adjustments and cleaning, a single machine can process both materials, adapting to their unique requirements.
No changes are needed when switching between PPR and PVC in injection molding.False
Differences in melting points and processing needs require temperature adjustments and thorough cleaning to prevent contamination.
- 1. What Are PPR and PVC Fittings?
- 2. Can Injection Molding Machines Handle Both Materials?
- 3. What Are the Steps in the Injection Molding Process for PPR and PVC Fittings?
- 4. What Are the Key Considerations for Production?
- 5. What Are the Applications of PPR and PVC Fittings?
- 6. How Do PPR and PVC Fittings Compare in Cost and Performance?
- 7. Conclusion
What Are PPR and PVC Fittings?
PPR and PVC fittings are critical components in plumbing systems, each tailored to specific applications based on their material properties.

PPR fittings excel in hot water systems2 due to their heat resistance, while PVC fittings dominate in cold water, drainage, and irrigation thanks to their durability and corrosion resistance.
| Material | Melting Point | Typical Applications | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| PPR3 | 160-170°C | Hot water systems | Flexible, heat-resistant |
| PVC4 | 100-150°C | Cold water, drainage | Rigid, corrosion-resistant |
PPR Fittings
PPR, a type of polypropylene, is prized for its flexibility and ability to withstand high temperatures (up to 95°C). It’s commonly used in residential and commercial hot water systems, including heating applications like radiant floor systems.
PVC Fittings
PVC, a robust thermoplastic, shines in cold water supply, sewage, and irrigation systems. Its rigidity and resistance to chemicals and corrosion make it ideal for applications where temperatures remain below 60°C.
PPR fittings are suitable for cold water systems.True
While designed for hot water, PPR can handle cold water, though PVC is typically more cost-effective for such uses.
PVC fittings are ideal for high-temperature applications.False
PVC degrades at elevated temperatures, making it unsuitable for hot water systems.
Can Injection Molding Machines Handle Both Materials?
The short answer is yes, but it’s not without considerations.
Injection molding5 machines can produce both PPR and PVC fittings, provided adjustments account for differing melting points, cleaning prevents contamination, and corrosion-resistant parts are used for PVC.

Material Compatibility
Both PPR and PVC are thermoplastics compatible with injection molding. However, PPR requires higher processing temperatures (200-250°C) than PVC (160-180°C). Additionally, PVC can release hydrogen chloride gas if overheated, posing a corrosion risk to standard machine components.
Machine Adjustments
Switching between materials demands:
-
Temperature recalibration: Higher for PPR, lower and tightly controlled for PVC.
-
Cleaning: Thorough purging of the barrel and screw to avoid cross-contamination.
-
Ventilation and corrosion resistance: Essential for PVC to manage gas emissions and protect equipment.
PVC processing requires corrosion-resistant machine parts.True
PVC’s potential to release corrosive gases necessitates specialized components, unlike PPR.
Switching between PPR and PVC requires no downtime.False
Cleaning and setup adjustments between materials take time to ensure quality output.
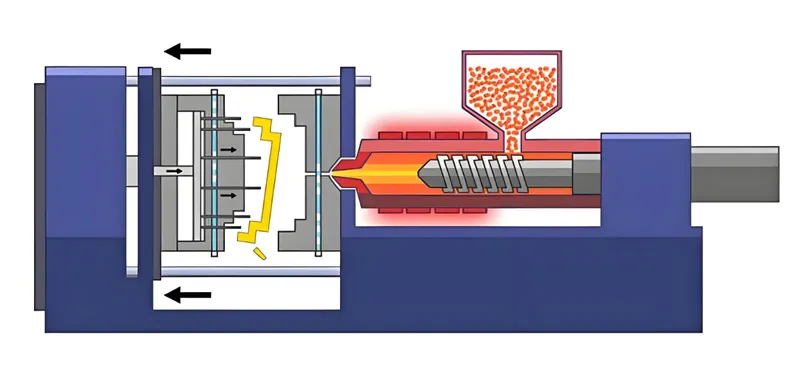
What Are the Steps in the Injection Molding Process for PPR and PVC Fittings?
The injection molding process6 follows a standard workflow, tailored to each material’s needs.
The process includes material preparation7, melting, injection, cooling, and ejection, with specific parameters adjusted for PPR’s higher heat tolerance and PVC’s sensitivity.

1. Material Preparation
-
PPR: Load dry pellets (low moisture absorption).
-
PVC: Add stabilizers to prevent decomposition.
2. Melting
-
PPR: 200-250°C in the barrel.
-
PVC: 160-180°C, with strict control to avoid gas release.
3. Injection
Inject molten material into the mold:
-
Pressure: Up to 100 MPa for PVC; varies for PPR.
-
Gate design: Ensures even filling.
4. Cooling
-
PPR: Higher cooling temps due to its melting point.
-
PVC: 70-130°F, managing shrinkage.
5. Ejection
Eject the solidified fitting, using 1-2° draft angles for ease.
Temperature settings are identical for PPR and PVC.False
PPR demands higher temperatures than PVC, requiring distinct barrel settings.
Cooling affects part quality for both materials.True
Proper cooling prevents warping and ensures dimensional accuracy.
What Are the Key Considerations for Production?
Success hinges on managing material-specific challenges.
Key factors include precise temperature control8, rigorous cleaning between runs, and corrosion-resistant parts for PVC to maintain quality and equipment health.

Temperature Control
-
PPR: Higher settings for melting and molding.
-
PVC: Lower, precise control to avoid decomposition.
Cleaning and Maintenance
-
Mandatory cleaning between material switches to prevent defects.
-
PVC processing requires regular checks for corrosion.

Design Considerations
-
PPR: Flexible designs with slight bends.
-
PVC: Rigid, precise dimensions.
Cleaning between PPR and PVC runs is optional.False
Skipping cleaning risks contamination and poor-quality fittings.
PVC poses unique maintenance challenges.True
Its corrosive potential requires resistant parts and ventilation.
What Are the Applications of PPR and PVC Fittings?
Each material serves distinct markets.
PPR fittings are used in hot water systems, while PVC fittings support cold water, drainage, and irrigation.

PPR Applications
-
Hot water plumbing (residential/commercial).
-
Heating systems (e.g., radiant floors).
-
Industrial fluid transport (heat-resistant).
PVC Applications
-
Cold water supply.
-
Sewage and drainage.
-
Irrigation systems.
PPR is exclusively for hot water.False
It can be used for cold water, though less common.
PVC excels in drainage due to its rigidity.True
Its durability suits harsh environments like sewage.
How Do PPR and PVC Fittings Compare in Cost and Performance?
Cost and performance guide material choice.
PPR is pricier but excels in heat resistance; PVC is cost-effective and durable for cold applications.

Cost
-
PPR: Higher due to material and processing needs.
-
PVC: Lower, ideal for large-scale projects.
Performance
-
PPR: Flexible, long-lasting in hot systems.
-
PVC: Rigid, chemically resistant in cold settings.
PPR is more expensive than PVC.True
Its specialized properties increase costs.
PVC outperforms PPR in heat resistance.False
PPR is designed for heat, unlike PVC.
Conclusion
Injection molding machines can indeed produce both PPR and PVC fittings, but success requires careful adjustments. From temperature settings to cleaning protocols and corrosion management, understanding each material’s needs ensures high-quality output. Whether crafting heat-resistant PPR fittings9 for hot water systems or durable PVC fittings for drainage, injection molding offers a versatile solution for modern manufacturing.
-
Learn about PVC fittings’ durability and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for cold water and drainage systems. ↩
-
Discover the best materials for hot water systems to ensure efficiency and longevity in plumbing applications. ↩
-
Explore the advantages of PPR in hot water systems, including its flexibility and heat resistance, to understand its applications better. ↩
-
Learn about PVC’s rigidity and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for cold water supply and drainage applications. ↩
-
Discover the intricacies of injection molding for PPR and PVC, including temperature adjustments and material compatibility. ↩
-
Understanding the injection molding process is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and material usage. ↩
-
Proper material preparation is essential for achieving high-quality molded products and minimizing defects. ↩
-
Temperature control is vital for ensuring product quality and preventing material degradation during molding. ↩
-
Explore the benefits of PPR fittings for hot water systems, including heat resistance and durability, to make informed choices for plumbing projects. ↩




